Abstract
The study investigates the effectiveness of Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) in Public sector colleges of Pakistan. The experimental study traces improvement in comprehension and writing skills of intermediate level students (studying in grades 11 and 12). An experiment group and a control group are used to study the effects of CLT on learners’ progress. A pre-test and post-test are carried out to measure any improvement in the students’ cognitive learning process. The experiment group is given treatment through vigorous intervention of CLT based activities. The control group is taught through the traditional method of GTM. The data collected from the two groups are analyzed using SPSS. The results show a significant improvement in the learning process, comprehension and writing skills of the students in the experiment group. The analysis proves the appropriateness of CLT for Pakistani ESL context.
Key Words
CLT, Experimental Design, ESL, GMT, Intermediate Level Learners, Pakistani Context.
Introduction
Technological developments have led to the emergence of new communication means to connect people in different parts of the world. As the world has become a global village, for individuals to succeed and participate in the world market has become inevitable to develop English language proficiency. Proficient speakers have improved writing and speaking skills, which serve their purpose of professional and academic interactions.
It has been observed that L2 students with poor writing skills often struggle in their academic careers. Almost for ten years the students in Pakistan are exposed to English as second language (L2) in formal school education. Nevertheless, after ten years of formal education, the majority of them exhibit poor writing skills. These students often lack exposure to authentic English language both inside outside their classrooms. Moreover, traditional teaching methods, such as the Grammar Translation Method (GTM) are applied in language classrooms, which is an obsolete pedagogical approach and has no use in language schools around the world. The impact of this outdated teaching approach can be seen in the learners’ lack of motivation in English lessons. For these reasons, we were interested to suggest CLT as an alternative approach to help Pakistani ESL learners improve their English proficiency and compete in international market.
There seems to be inadequate research on the implementation of CLT based pedagogy in teaching of narrative to low proficiency Pakistani students in Public sector. The purpose of the present research is to explore the usefulness of CLT in Pakistani context. This study seeks answers to the following research questions and tests the two hypotheses to investigate the effectiveness of CLT in Pakistani context.
1. To what extent the subjects’ learning process improve, comparing their ability before and after the strategy employed?
2. Does it enable the focus of the learners to shift from rote learning towards critical thinking and analysis?
Hypotheses
Null Hypothesis: It is hypothesized that employing and incorporating of CLT activities in the teaching of novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips” might not prove effective in increasing the level of students’ learning proficiency.
Hypothesis: It is hypothesized that motivating students in active thinking and creative problem-solving approach in the teaching of novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips” might benefit and increase the level of students’ learning proficiency.
Literature Review
Since its origin and initiation in Europe in the 1970s, CLT has acquired increasing popularity and worldwide recognition as an approach to language teaching that contributes to learners' communicative competence and addresses the inadequate emphasis of traditional methods on communication skills. The spread of CLT from its birthplace in Western countries to its new home in non-Western countries such as Pakistan, has drawn considerable attention from researchers and practitioners in the field of ELT resulting in several research studies conducted to investigate its appropriacy and implementation ESL/EFL contexts. Although most of the literature lends support to CLT in ESL/EFL contexts, much of the research on CLT innovations in ESL/EFL contexts associates various challenges with its implementation in ESL/EFL classrooms (Canale & Swaine , 1980; Ellis, 1996; Savignon, 1991). This section of the paper reviews literature on the effectiveness of CLT along with the challenges ESL/EFL teachers may face in introducing CLT into their classrooms.
Communicative Language Teaching
The essence of CLT lies in unification of pedagogical approaches and curricula that encircle both the objectives of language learning and the teaching procedures of classroom learning. It is important that the teaching methodologies involve view competence in terms of social interaction and focus on communication of language in terms of form and function (Savignon, 1991).
In communicative classroom activities the teachers encourage the learners to take risks and speak in innovative way. A collection of role plays, games, pair work, group activities/discussions and other communicative activities include CLT based teaching. The notion of communication and negotiation of meaning help teachers to incorporate interactive activities in classroom.
CLT approaches language learning and teaching in a multidisciplinary perspective involving psychology, sociology, linguistics and educational research. It demands a cognitive involvement in the process of learning and acquisition. Hence, the methods, activities, instructional materials and resource selection depend on the learners’ needs and styles of learning.
CLT emphasizes student-centered learning (Parrish, 2004), which encourages students to take on more active roles and engage in role plays and debates that help them negotiate meaning according to situational needs. These tasks contribute to the central aim of CLT; that is, the achievement of “functional communicative ability” – making the learner capable of actively using comprehensible language and communicating according to the varying situations. In CLT syllabus the students are put in real life like situation whereas they should demonstrate the application and function of language in a variety of context. There is no fixed technique taken as the standard authority in CLT. Instead, it tends to encourage the use of a variety of materials, teaching methods and techniques that are appropriate according to the context and can be suitably moulded for language learning, provided that the focus remains on functional use of language in context and not solely on form (Brandl, 2008; Richards & Rodgers, 2001).
Meaning is paramount in CLT. Contextualization and judicious use of native language is permitted when the need arises. Its flexibility allows for translations in the class where it becomes necessary to communicate the meanings to the learners. It focuses on the learning of language through trial and error. It points toward a “learning by doing” or the “experience approach”, a process which leads to communicative competence (Richards & Rodgers, 2014).
Form and Function in CLT Activities
It is to be understood that in negotiation of meaning in a teaching methodology such as CLT, the importance of form cannot be ignored. The comprehension and conveyance of meaning only without an appropriate form might not be successful in a modern classroom setting demands. The research emphatically support the incorporation of meaning-focused experience with form-function exercises (Savignon, 1991).
In terms of assessment, Swain (1988) suggests that on the spot correction of errors will impede the process of learning. This will slow down the learning process and hamper the learning of students by extracting a negative effect on the learning environment in a CLT based classroom. Compared with classrooms where traditional teaching methodologies prevail, focusing on the learning of academic content and a second language as their major goals, the traditional teaching of content may functionally restrict a teacher’s use of language in certain ways. If teacher centers upon the correction of content, the correction of form shifts to the background, in order to preserve the communicative flow. On the other hand, if the focus shifts and the emphasis is only on second language learning with accuracy and preciseness of form and structure as priority, the meaning-orientation might slip in the background. As a consequence, the students' opportunities to engage in extended discourse get limited. To make the procedure of second language learning interesting and significant, it is important to find out ways to adapt content teaching according to the needs of second language learning process.
Appropriateness of CLT
CLT in ESL contexts is controversial due its appropriateness in various language teaching settings. It has been recommended that a solid need for a contextual approach is required, rather than emphasizing upon CLT approach as a complete picture. The aspects of contexts involve learners’ attitudes towards the target language, cultural differences, expectations and norms that sometimes play more important role than the methods of teaching (Lee, 2014).
A recent research conducted in Pakistan by Ahmed and Rao (2013) investigated the usefulness of CLT based pedagogy and its impact on students’ achievement and attitude. The study empirically traced the improvement in the achievement of students in comprehension, vocabulary, and essay writing and speaking. The qualitative part of their study analyzed the attitude of the teachers towards the implementation of CLT in the scenario of Pakistan where the major pedagogical approach followed is the GTM. Both the phases of this study propagated the idea that the teachers as well as the students had the ability to shift their focus from the traditional and archaic teaching methods towards newer and better approaches; such as CLT based teaching.
CLT based Teaching Using Narratives
Research indicates that stories or a story told in a novel have a specific pattern which asks for particular kind of information and logical relationships. The sequence of the narrative whether it is in the form of drama or novel has been stressed since the time of Aristotle. Narratives are about characters and their actions which are arranged in a sequence and are interwoven (Temple & Gillet, 1989).
It is important to select a novel for teaching purpose that is based on a fully articulated story that motivates the learners. It must include all requirements of novel; background setting, characters, sequential action leading toward goals, reasons behind these actions, significance, main theme; all in a well woven frame work. This intricate fabric of writing becomes a mean of understanding meaning of human nature and life. Narrative is a study of how meaning is taken out from human experience (Clandinin & Connelley, 1989). The novel provides a compelling context for learning. Each of our lives is a story, a living narrative of our existence. Thus, a narrative simply becomes a study of life. Taking it on simpler plain of meaning, if we relate to someone how we had spent our summer vacation, how enjoyable the trip to Disney Land was, or how the boating trip was made memorable, where we stayed, the people we met, we do it as a story. In this way stories are easy for learners to understand because they are based on a simple, understandable structure. Stories have believable characters, which we can easily relate to, that present solutions to different problems, a pattern analogous to life and an instinctual bonding is developed between the learners and the characters of a narrative. As the characters in the novel are confronted with circumstances, trials, perceptions and insights, readers share in their emotions, bask in happiness with them, cry in grief, feel joy in their achievements and fear in anticipation, and triumph in their success. This bonding allows the learners to experience the lives and feelings of narrative characters sympathetically and develop perception of their own lives during the process of learning.
Learners integrate their life experiences with narrative characters as narratives are a means of associating oneself with organized events turning it into meaningful experiences. So, novels provide learners a platform for making meaning, rediscover their own reality in deep and meaningful understanding (Bruner, 1990). Bruner (1990) establishes that the narratives are strong tool of learning. The benefit of teaching through the medium of novel is that it has the power to convey concepts related to the story in an effective way that can never be ignored by the learners. Moreover, it casts a long-term impression on the minds of the learners. Using literature in EFL curricula offers the benefits of developing EFL learners’ awareness of language usage as well as contributing to understanding. Prose fiction, also termed as “novel”, is widely popular among people from all walks of life, which engages the readers’ imagination and gives students motivation to read further as they feel the joy and satisfaction from reading it. Moreover, it enables to enhance their learning capabilities thus making them intuitive learners.
Methodology
The experimental method in research assumed a formal place in educational psychology with the classic studies (Morrison & Ross, 1996). The experimental research focuses on measuring the variables. It demands approaches where all the possible variables could be controlled in order to explore the effect of one ‘independent variable’. This interest to explore the effect of a change in a certain condition is referred to as ‘treatment’. Morrison and Ross (1996) point out that standardized procedures have to be used to control the variable in order to study the effect of the treatment. This standardization ensures high internal validity in achieving the results on the dependent variable, while making a comparison between the Experimental group and the Control group.
The researchers carried out an experimental study in the domain of teaching narrative to intermediate students at a government college in Lahore. The narrative selected for teaching will be “Goodbye Mr. Chips” which is a part of the syllabus assigned to intermediate form Part II students. The novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips” is a classic novel encompassing the changes brought about by the turn of the century. The novel is taught to the students in a traditional approach towards teaching. The students are tested mostly on the base of their memory as the questions are designed on the lowest level of Bloom’s taxonomy of learning; knowledge. The novel was taught employing activities related to CLT.
The teaching methodologies used for the experimental group A and control group B act as the independent variable. Group A received treatment where the task-based activities of CLT to be applied appropriately to the learning environment. The effect of independent variable on the learning achievement (dependent variable) of the students was tested with the help of post-test designed according to the six levels of Bloom’s taxonomy of cognitive learning domain. A similar pre-test was conducted earlier to check the level of students’ comprehension and proficiency in the understanding of novel. Mainly, this experimental study explored the effect of teaching methodologies on the learning achievement of ESL students.
Sampling
The research was carried out on two groups of intermediate level of learners in a
government college. A group comprised of 50 female students of intermediate level part 11 was selected (Arts group). All students have attended 5 years in English medium at secondary level. As an experimental study, two groups of female students are divided into experimental and control groups who are between 15–16 years of age. All students belong to Arts group who are selected by applying systematic random sampling. The variables such as age, gender and educational background are controlled.
Data Collection Tools
The study included the following variables:
1. The independent variable represented in the CLT based instruction of the novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips”
2. The dependent variable represented in the Intermediate students’ comprehension writing skills and retention that will be measured through the clarity of the “Sentence structure” of the written answers, the “Vocabulary” and “Grammar”.
We used the following instruments to move on with the experimental study:
Pre-test: A Pre-test based and designed on Bloom’s taxonomy of cognitive learning process specifically related to the novel, “Goodbye Mr. Chips” to establish a niche for experimenting with the pedagogical technique applied to the teaching of narrative. The pre-test included questions on the novel’s structure and form, themes and characters as well as the plot and movement of the story. The assessment included subjects’ ability to produce answers correctly through sentence structure, grammar and vocabulary.
Post-test: A Post-test based on the experimental pedagogical technique, in this case, CLT. Discourse Completion Task (DCT) was effectively integrated in the post-test to check the comprehension of the subjects on the three selected criteria of assessment (Grammar, sentence structure and vocabulary). The post-test was also based on Bloom’s taxonomy of learning levels to measure the extent of improvement in the subjects’ comprehension and understanding. It was an effective tool to observe and trace any enhanced learning abilities developed in the subjects at the end of the experiment.
The following Hypotheses were developed:
Hypothesis: Employing and incorporating of CLT activities in the teaching of novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips” might not prove effective in increasing the level of students’ learning proficiency.
Hypothesis: Motivating students in active thinking and creative problem-solving approach in the teaching of novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips” might benefit and increase the level of students’ learning proficiency.
Data Collection Procedure (Intervention Test)
In order to collect data, eight weeks of teacher intervention plane was developed.
Detailed lesson plans were designed for teaching comprehension and writing skills through CLT based approach with the experimental group. The lessons during the experiment focused on the basic initial approach to CLT; including IRE sessions, pair work/ group work, discussions, presentations and role-plays. Twelve chapters were chosen from the era based novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips”. Time was allocated accordingly to each chapter which was spread over a period of two months. During the eight weeks of teacher intervention test, the students’ responses were noted down in order to determine whether they showed any interest in what was taught to them, were they motivated to learn new language items and was there any difference between the attitude of both the experimental group and control group towards learning through CLT based approach to writing skills. The purpose of noting down students’ attitudes in both the classes were to ascertain whether the CLT based instruction was making any difference in motivating the students to learn English language or not.
During lesson one the teacher introduced to the students the teaching pedagogy that they will be exposed to during the following two months. This was necessary so as to prepare the students on the physical as well as cognitive level for the challenges of the various tasks that they will have to face during the experimental phase. Starting from the basic, IRE session helped to prepare the students from the easiest task of thinking and communicating creatively. The IRE session included oral as well as written practice so that all four skills of comprehension and communication could be involved step by step. The feedback from the teacher allowed for the students to make corrections during their oral and written participation. The teacher specifically explored language features including learning of vocabulary and its use, the structure of a narrative text (i.e. use of verbs and connectives) with her students. The purpose of this was to draw the attention of the students of experimental group towards the linguistic features and their use of grammar in basic sentence of a narrative text.
In Lesson 2, the teacher discussed in detail the structure of a narrative by taking examples from the texts based on synonymous vocabulary, grammar and the role of sentence structure. The difference between dialogues and the passive sentence structure was discussed. The worksheets were designed to make the subjects participate by discussing with each other the use of best possible vocabulary, most suitable sentence structure and the appropriate grammatical features.
In Lesson 3, the teacher discussed with the students, the importance of role plays in learning a language. Based on the previous exercise of differentiating between dialogues and passive writing, the students were guided to write their own dialogues using the vocabulary and the techniques of sentence structure with appropriate grammar related to the characters of the novel. They were encouraged to select characters of their own choice and create their dialogues. This practice involved high order cognitive skills to be put into practice and exhibit their communication skills. This laborious exercise encouraged the subjects to freely communicate with their instructor as well as with their peers.
In Lesson 4, students were given the task of presentations in pairs. The purpose of this activity was to make the students practice the vocabulary, the form and function of the language as they had been exposed to vigorous exercises concerning the form and function of English language. The questions/answer session at the end of each presentation would allow them to reply after assessing the information required by the question exhibiting their comprehension level along with the communicative skills. At first, the teacher offered explicit information on the technique of presentation and guided the subjects in selecting important incidents that had occurred in the narrative within the 12 chapters. Then, the students were asked to construct sentences using the vocabulary words taken out from the text. The students were divided into pairs with one weak student and one slightly better student based on their pre-test results. The purpose of dividing students into pairs was to facilitate peer learning as well as learning from the teacher. Research shows that learners can perform at a higher level by working together in groups and with expert guidance of the teacher as compared to when they perform individually on their own (Donato, 2000; Ohta, 2000, as cited in Hyland, 2007). One of the dominant characteristics of genre based pedagogy is the role of the facilitator who can either be the teacher or a better skilled peer.
Throughout the experimental phase, students practiced different tenses; they tried to convert their sentences into past and future tense. The frequent IRE sessions allowed the students to freely practice sentence structure and appropriate grammatical expressions. The teacher provided explicit grammatical based lessons to help the students restructure their language from spoken to written mode. The lessons incorporated intensive practice of grammatical features specific to each tense. The teacher discussed in detail the present, past and future tense with the students by taking out examples from the specific text; “Goodbye Mr. Chips”. Despite intensive grammar instructions, it was noticed that the students found it difficult to grasp some very basic structural linguistic features. For example, the use of did and second form of verb was a common mistake in their writings, also most of the students confused their “s” and “es” while using present tense. The students didn’t grasp the suitable use of some modal verbs (i.e., must vs. should) and its use was a huge challenge to the students. The purpose of this incorporated activity throughout the experiment was to make the students practice writing appropriate sentences in English. In this way the students practiced not only communicating in English in its proper form but also practiced writing sentences according to the grammar rules. Gradually, this would lead to minimizing the teacher’s role and directing the students’ progress from the role of a passive recipient to that of an autonomous learner. In the context of this study the aim of the teacher was to work with the students to understand, learn and communicate in an ESL environment. Although the students began to realize the importance of framing the structure of a sentence keeping in mind the suitable vocabulary and appropriate grammar rather than just ‘jumping into writing’, still, the subjects needed more practice. The consistent feedback from the teacher to the students about their participation and discussions regarding room for improvement in every activity was necessary.
While the experimental group was taught the narrative “Goodbye Mr. Chips” with carefully planned CLT based instructions including flexible task based activities to improve their communicative and written skills, the control group on the other hand was taught the novel using the traditional method of pedagogy. In the traditional method, students were given lectures and almost every word of the narrative was translated for them. The students of the controlled group were made to write the important questions from each chapter and the answers were also pointed out to them. The teacher gave these students oral tests based on important informative questions and they were instructed to memorize them. The teacher made sure that the students had crammed the vocabulary, with special focus on spellings, and the sentence structures from the text. In the final phase of traditional pedagogy with the experimental group, students of the control group were asked to reproduce the answers that they had memorized.
The same process was repeated for eight weeks with the 12 chapters one by one. During the implementation of CLT based pedagogy with the Experimental group the teacher noted down that students’ interest was raised in the lessons, they were keen to learn new concepts and were better able to comprehend all the grammatical rules that they had been learning in their classrooms but had had trouble in implementing. However, the teacher noticed that the students of control group’s interest were not as high as it was observed in the experimental group. The teacher observed that the students of controlled group were putting their energies into trying to cram the information instead of trying to comprehend the meaning. On the other hand, the students of experimental group not only exhibited a better understanding of grammar and spelling but at the same time the teacher observed her students using the same grammatical rules more confidently.
Data Analysis
The score of the students were studied separately for each student based on pre-test and post-test and the percentage of each student’s achievement was measured. A correlation was formed to measure the effect of independent variable using SPSS. Each participant was assigned a code. The score on each question in the pre-test was compared with the score on the questions in post-test. This allowed for an extensive insight into each student’s learning capability and improvement in proficiency.
The difference of achievement scores for both the groups; experimental and control was calculated. The mean score of the experimental group in the pre-test was compared with the mean of their performance in post-test. Similar measures were taken for the control group. The mean for the performance of experimental group was compared with the mean for the performance of the control group. Mean percentage was calculated to further clarify the results. These comprehensive analyses were helpful to identify the gap and shortcomings in the teaching methodologies being practiced in the government colleges.
Findings
Data
Representation of Pre- test
Before beginning with the intervention, it was decided to conduct
a pre-test with both the control group and the experimental group. In this
pre-test the students were asked to write answers to questions based on the
first 12 chapters of the novel, “Goodbye Mr. Chips” to see their proficiency in
English comprehension skills. Three dependent variables (Vocabulary, Grammar
and Sentence Structure) were identified to judge the comprehension and proficiency
level of writing skills of the students. Prior to the test, the students of
experimental group and control group were shared the areas in which their
comprehension and writing skills were to be assessed.
The data analysis of pre-test scores of both the experimental and
the control group shows that there was little difference in the scores
regarding all the three dependent variables that were identified to assess
their writing skills. The mean of the test scores of both the experimental
group and control group in vocabulary was 1.84 and 1.68 respectively, whereas
in grammar the mean of experimental group and control group was 2.28 and 2.16
respectively. In sentence structure, the mean of both the groups was 2.32 and
2.20 respectively (Table 1). The above-mentioned data clearly indicate that
both the groups were quite similar in their proficiency level regarding these
three dependent variables of comprehension and writing skills proficiency.
Table 1. Pre-test Scores of Experimental
Group and Control Group
|
S. N |
Variables |
Experimental (n=25) |
Control (n=25) |
||
|
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
||
|
1. |
Pre-Vocabulary
|
1.84 |
.688 |
1.68 |
.476 |
|
2. |
Pre-Grammar |
2.28 |
.843 |
2.16 |
.624 |
|
3. |
Pre-Sentence Structure |
2.32 |
.900 |
2.20 |
.645 |
|
4. |
Pre-total |
6.44 |
2.43 |
6.04 |
1.74 |
It was important to use groups of students that are at the same
proficiency level in English comprehension and writing skills so that the data
collected after the experiment is comparable. For this purpose, the pre-test
was an important research tool to achieve internal validity.
Paired
Sample t test (Control Group and Experimental Group)
Paired Sample test was applied on data to find the differences between pre-and post-test scores for both the control and the experimental groups. In vocabulary, there was no difference found between the pre-test score and the post-test score of control group. In grammar and sentence structure and total of the test score, significant statistical improvements were found between pre-test and post-test. The statistical data analysis clearly shows that the Control group performed better in their post-test scores as compared to their pre-test scores in two out of the total three identified areas of study as indicated by the p value. It should be noted here that the Control Group was taught comprehension and writing skills using the traditional method of instruction where the subjects were passive recipients of the information transmitted by the teacher.
Table 2. Paired Sample t-test (Control Group & Experimental Group)
Paired
Sample t test (Experimental Group)
Paired Sample test was applied on data to find the differences
between pre-and post-test scores of the experimental group. In all areas;
vocabulary, grammar, and sentence structure, significant improvements were
found between pre-test scores and post-test scores as indicated by their P
values (Table 2). The data analysis clearly shows that the experimental group
performed better in their Post-test scores as compared to their pre-test scores
in all three identified areas. The experimental group went through a period of
eight weeks task-based teaching of the novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips”.
Frequency
Tables for Variables
To further clarify the difference between the scores of the
pre-test and post-test of control group and the experimental group, in each
area of study, frequency tables were generated with graphs for each variable.
Table 3.
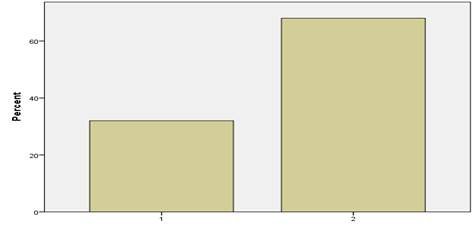
Frequency Table Showing Pre-test Control Group (Vocabulary)
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid
Percent |
Cumulative
Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
8 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
|
2 |
17 |
68.0 |
68.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Findings
Data
Representation of Pre- test
Before beginning with the intervention, it was decided to conduct
a pre-test with both the control group and the experimental group. In this
pre-test the students were asked to write answers to questions based on the
first 12 chapters of the novel, “Goodbye Mr. Chips” to see their proficiency in
English comprehension skills. Three dependent variables (Vocabulary, Grammar
and Sentence Structure) were identified to judge the comprehension and proficiency
level of writing skills of the students. Prior to the test, the students of
experimental group and control group were shared the areas in which their
comprehension and writing skills were to be assessed.
The data analysis of pre-test scores of both the experimental and
the control group shows that there was little difference in the scores
regarding all the three dependent variables that were identified to assess
their writing skills. The mean of the test scores of both the experimental
group and control group in vocabulary was 1.84 and 1.68 respectively, whereas
in grammar the mean of experimental group and control group was 2.28 and 2.16
respectively. In sentence structure, the mean of both the groups was 2.32 and
2.20 respectively (Table 1). The above-mentioned data clearly indicate that
both the groups were quite similar in their proficiency level regarding these
three dependent variables of comprehension and writing skills proficiency.
Table 1. Pre-test Scores of Experimental
Group and Control Group
|
S. N |
Variables |
Experimental (n=25) |
Control (n=25) |
||
|
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
||
|
1. |
Pre-Vocabulary
|
1.84 |
.688 |
1.68 |
.476 |
|
2. |
Pre-Grammar |
2.28 |
.843 |
2.16 |
.624 |
|
3. |
Pre-Sentence Structure |
2.32 |
.900 |
2.20 |
.645 |
|
4. |
Pre-total |
6.44 |
2.43 |
6.04 |
1.74 |
It was important to use groups of students that are at the same
proficiency level in English comprehension and writing skills so that the data
collected after the experiment is comparable. For this purpose, the pre-test
was an important research tool to achieve internal validity.
Paired
Sample t test (Control Group and Experimental Group)
Paired Sample test was applied on data to find the differences between pre-and post-test scores for both the control and the experimental groups. In vocabulary, there was no difference found between the pre-test score and the post-test score of control group. In grammar and sentence structure and total of the test score, significant statistical improvements were found between pre-test and post-test. The statistical data analysis clearly shows that the Control group performed better in their post-test scores as compared to their pre-test scores in two out of the total three identified areas of study as indicated by the p value. It should be noted here that the Control Group was taught comprehension and writing skills using the traditional method of instruction where the subjects were passive recipients of the information transmitted by the teacher.
Table 2. Paired Sample t-test (Control Group & Experimental Group)
Paired
Sample t test (Experimental Group)
Paired Sample test was applied on data to find the differences
between pre-and post-test scores of the experimental group. In all areas;
vocabulary, grammar, and sentence structure, significant improvements were
found between pre-test scores and post-test scores as indicated by their P
values (Table 2). The data analysis clearly shows that the experimental group
performed better in their Post-test scores as compared to their pre-test scores
in all three identified areas. The experimental group went through a period of
eight weeks task-based teaching of the novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips”.
Frequency
Tables for Variables
To further clarify the difference between the scores of the
pre-test and post-test of control group and the experimental group, in each
area of study, frequency tables were generated with graphs for each variable.
Table 3.
Frequency Table Showing Pre-test Control Group (Vocabulary)
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid
Percent |
Cumulative
Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
8 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
|
2 |
17 |
68.0 |
68.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Findings
Data
Representation of Pre- test
Before beginning with the intervention, it was decided to conduct
a pre-test with both the control group and the experimental group. In this
pre-test the students were asked to write answers to questions based on the
first 12 chapters of the novel, “Goodbye Mr. Chips” to see their proficiency in
English comprehension skills. Three dependent variables (Vocabulary, Grammar
and Sentence Structure) were identified to judge the comprehension and proficiency
level of writing skills of the students. Prior to the test, the students of
experimental group and control group were shared the areas in which their
comprehension and writing skills were to be assessed.
The data analysis of pre-test scores of both the experimental and
the control group shows that there was little difference in the scores
regarding all the three dependent variables that were identified to assess
their writing skills. The mean of the test scores of both the experimental
group and control group in vocabulary was 1.84 and 1.68 respectively, whereas
in grammar the mean of experimental group and control group was 2.28 and 2.16
respectively. In sentence structure, the mean of both the groups was 2.32 and
2.20 respectively (Table 1). The above-mentioned data clearly indicate that
both the groups were quite similar in their proficiency level regarding these
three dependent variables of comprehension and writing skills proficiency.
Table 1. Pre-test Scores of Experimental
Group and Control Group
|
S. N |
Variables |
Experimental (n=25) |
Control (n=25) |
||
|
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
||
|
1. |
Pre-Vocabulary
|
1.84 |
.688 |
1.68 |
.476 |
|
2. |
Pre-Grammar |
2.28 |
.843 |
2.16 |
.624 |
|
3. |
Pre-Sentence Structure |
2.32 |
.900 |
2.20 |
.645 |
|
4. |
Pre-total |
6.44 |
2.43 |
6.04 |
1.74 |
It was important to use groups of students that are at the same
proficiency level in English comprehension and writing skills so that the data
collected after the experiment is comparable. For this purpose, the pre-test
was an important research tool to achieve internal validity.
Paired
Sample t test (Control Group and Experimental Group)
Paired Sample test was applied on data to find the differences between pre-and post-test scores for both the control and the experimental groups. In vocabulary, there was no difference found between the pre-test score and the post-test score of control group. In grammar and sentence structure and total of the test score, significant statistical improvements were found between pre-test and post-test. The statistical data analysis clearly shows that the Control group performed better in their post-test scores as compared to their pre-test scores in two out of the total three identified areas of study as indicated by the p value. It should be noted here that the Control Group was taught comprehension and writing skills using the traditional method of instruction where the subjects were passive recipients of the information transmitted by the teacher.
Table 2. Paired Sample t-test (Control Group & Experimental Group)
Paired
Sample t test (Experimental Group)
Paired Sample test was applied on data to find the differences
between pre-and post-test scores of the experimental group. In all areas;
vocabulary, grammar, and sentence structure, significant improvements were
found between pre-test scores and post-test scores as indicated by their P
values (Table 2). The data analysis clearly shows that the experimental group
performed better in their Post-test scores as compared to their pre-test scores
in all three identified areas. The experimental group went through a period of
eight weeks task-based teaching of the novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips”.
Frequency
Tables for Variables
To further clarify the difference between the scores of the
pre-test and post-test of control group and the experimental group, in each
area of study, frequency tables were generated with graphs for each variable.
Table 3.
Frequency Table Showing Pre-test Control Group (Vocabulary)
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid
Percent |
Cumulative
Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
8 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
|
2 |
17 |
68.0 |
68.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Figure 1
Graph Representing Pre-test Control Group (Vocabulary)
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid
Percent |
Cumulative
Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
8 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
|
2 |
17 |
68.0 |
68.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Figure 2
Bar Graph for Post-test Control Group (Vocabulary)
The frequency table and the bar graph clearly show that there is no difference in the scores of the pre-test and post-test concerning the variable Vocabulary for the Control group. The traditional model of teaching could not bring any significant change in the subjects’ proficiency level. The percentage shows no deviation resting at 32 % and 68 %.
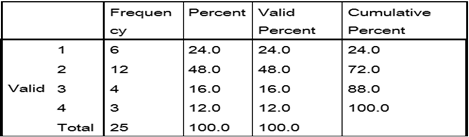
Table 5. Frequency for Pre-test Control Group (Grammar)
Figure 3
Bar Graph Showing Percentage for Pre-test Control Group Grammar
Table 6. Frequency for Post-test Control Group Grammar
Figure 4
Bar Graph Displaying Post-test Control Group Grammar
The
frequency table and the bar graph for the variable grammar for control group
shows a difference between the scores where 44 % of the participants have shown
improvement while reproducing the text that they had been cramming as guided by
their instructor.
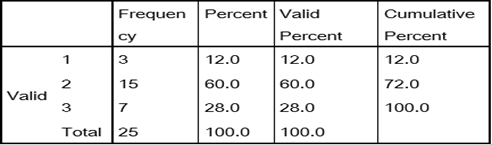
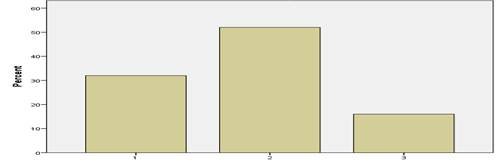
Table
7. Frequency for Pre-test Control Group Sentence Structure
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid
Percent |
Cumulative
Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
3 |
12.0 |
12.0 |
12.0 |
|
2 |
14 |
56.0 |
56.0 |
68.0 |
|
|
3 |
8 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Figure 5
Bar graph for pre-test control group sentence structure
Table 8. Frequency for post-test control group sentence structure
Figure 6
Bar graph for post-test control
group sentence structure
Improvement can be seen in the Sentence structure which shows 44 % subjects of control group performing better in the post-test. However, a significant link can be formed here between the appropriate grammar in a sentence and the sentence structure as they are mutually linked. Memorizing the text as mentioned in the novel left little space for making mistakes. The improvement in the grammar and sentence structure co-related to an overall improvement in the post-test results.
Table 9. Frequency for pre-test experimental group vocabulary
Figure 7
bar graph pre-test experimental group vocabulary
Table 10. Frequency for post-test experimental group vocabulary
Figure 8
Bar Graph for Post-test Experimental Group Vocabulary
The
frequency table and the bar graph for the first variable vocabulary shows a
slight improvement in the subjects’ proficiency level who were exposed to the
experimental phase including CLT based teaching approach. 12 % of the students
performed better. The minimum percentage shows a slight improvement as in the
pre-test 32 % of the students were at the minimum score, which has been
decreased to a 24 % scoring minimum in the post-test.
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
6 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
|
2 |
6 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
48.0 |
|
|
3 |
13 |
52.0 |
52.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Figure 9
Bar Graph Pre-test Experimental Group Grammar
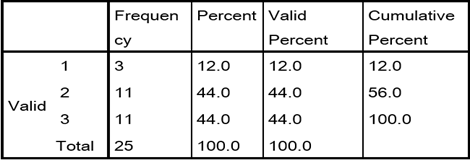
Table
12. Frequency for Post-test Experimental
Group Grammar
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
5 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
2 |
1 |
4.0 |
4.0 |
24.0 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
20.0 |
20. |
44.0 |
|
|
4 |
14 |
56.0 |
56.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Figure 10
Bar Graph for post-test Experimental Group Grammar
A
noticeable change can be traced in the area of grammar, where a higher
percentage of 14 has shown improvement in the use of appropriate grammar in the
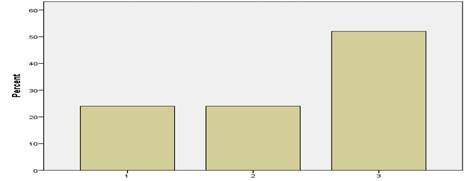
post-test results. The frequency table of the pre-test is evident of the fact
that the highest scoring subjects is limited to 52 % in the pre-test who could
not score more than 3 in this area.
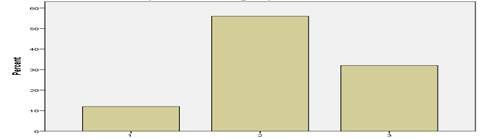
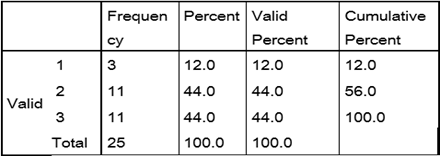
Table 13. Frequency for pre-test experimental group
sentence structure
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
6 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
|
2 |
6 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
48.0 |
|
|
3 |
12 |
48.0 |
48.0 |
96.0 |
|
|
4 |
1 |
4.0 |
4.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
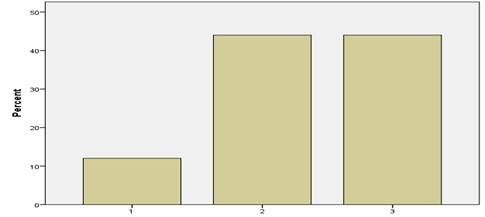
Figure 11
Bar graph Pre-test Experimental Group Sentence Structure
Table
14. Frequency for Post-test Experimental Group Sentence Structure
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
1 |
5 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
2 |
1 |
4.0 |
4.0 |
24.0 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
44.0 |
|
|
4 |
14 |
56.0 |
56.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Figure 12
Bar graph for experimental group sentence structure
The variable, sentence structure shows maximum improvement. The frequency table and the bar chart exhibit a leap from 4 % scoring highest in the pre-test to a 56 % scoring the best in the post-test. The students of the experimental group enhanced their proficiency level in the formation of sentences using appropriate grammatical features
It is hypothesized that motivating students in active thinking and creative problem-solving approach in the teaching of novel “Goodbye Mr. Chips” might benefit and increase the level of students’ learning proficiency.
The data analysis using the paired sample t-test supports the hypothesis as statistically significant differences were found between the scores of experimental group and control group in all three domains of the study; vocabulary, grammar and sentence structure as indicated by their frequency tables and bar charts. From the data analysis of the test scores, we can assume that CLT based instruction helped the students of the experimental group in enhancing their comprehension of the narrative and perform better in their writing skills as compared to the students of control group who were taught in a traditional manner mainly focusing on the transmission of information.
The experimental Group showed improvement in all three areas of study which may be attributed to an outcome of a vigorous inculcation of CLT based pedagogy. It is also worth noting that the students of control group did not show significant improvement in vocabulary. Experimental group showed significant improvement in their post-test scores in “vocabulary” as compared to the control group. It was interesting to note that students of control group showed improvement in their use of appropriate grammar and formation of sentences as compared to using a variety of vocabulary. This might be attributed to the fact that the students of control group were given a chance of cramming the provided text without any creative involvement and cognitive participation. Therefore, they reproduced the vocabulary that was given to them by the teacher. Whereas the students of experimental group scored better in their post-tests in vocabulary as they had been practicing synonyms in their initial lessons. The improvement in the use of appropriate grammar with the most suitable sentence structure in the post-test scores of experimental group as compared to their pre-tests displays a mutual link between the two variables. It was observed that they exhibited a better understanding of the sentence structures as compared to the students of the control group as they had been exposed to a consistent practice of communication keeping in mind the form and function of English as an ESL. The confidence level of the students while using the rules of grammar had also increased considerably. It can be stated that this intervention provided a major opportunity to the students of the group to shift their focus form cramming and rote learning towards critically analyzing the text. Based on the areas of this study that CLT based pedagogy encompassed, the students had a fair chance of changing their direction and focus of learning. This resulted in an enhanced proficiency level of students regarding their writing skills.
Discussion
The data elicited from the experimental phases of this study showed that CLT based pedagogy in the teaching of narrative was beneficial to low proficient ESL learners. The findings are consistent with the previous studies conducted by Beretta & Davies, (1985), Swain (1988), Sun & Cheng (2002) and Ahmed & Rao, (2013) who conducted similar studies to test the effectiveness of CLT based approach and reached similar conclusions in their respective studies
Key ESL pedagogical issues of public sector institutions of Lahore
The findings helped in identifying key ESL pedagogical issues of public sector institutions in Pakistan. The method of instruction in these institutions is archaic and needs to be revised. There is no doubt about the fact that the mode of instruction in these institutions is closer to the GTM. This method has been viewed skeptically in the modern language teaching approaches, but the public sector institutions are still following the same obsolete pedagogical methods which may appear to be one of the biggest reasons for students’ reluctance to communicate in English language. The shift from transmitting information from the teacher to the recipient through an eclectic approach appears to be a promising alternative for these low proficient ESL learners. The CLT based instruction may also help in providing these students with the exposure to the texts written in English language from which the students of these institutions are far removed. They do not bother themselves with reading texts in English which is the major reason for their lack of skill in writing comprehension.
Another advantage that CLT based instruction may provide is, it can also contribute towards raising the interest of the students in reading texts in English language instead of only relying on what the teacher is reading in class. Intensive and extensive reading techniques incorporated into CLT based teaching instruction can enhance the students’ comprehension level and can prove a stepping stone towards becoming an independent learner. Furthermore, this practice would affect the proficiency in their writing skills. Similar to the findings of Grab (2001), the present study also asserts the use of authentic material for reading in enhancing the writing proficiency of the students.
This study has shown that CLT based pedagogy is the perfect blend of language, content, and contexts as it enables the teachers to teach their students the foreign language the way it is used in real life situations. Hyland (2007) has discussed this benefit of using narrative to teach English in ESL classrooms as it enables the teachers to introduce the second language to students the way it is used in real life. The CLT based approach focused on the very basic and key features of teaching a narrative using IRE sessions, peer learning, pair work and group work, role plays and discussions. Students attempted to show their learning process through comprehension writing skills and the post-test scores of experimental group revealed that this procedure worked well for the low proficient students of this particular public sector college. The findings suggest that the comprehension and writing skills cannot be taught in a vacuum. It means that the students cannot understand and learn writing skills through some abstract rules about the use of language, in fact they need to contextualize the rules.
Benefits of CLT based instruction
The benefits of using CLT based instruction to teach ESL writing skills are highlighted according to findings of the study.
The impact of collaboration and scaffolding in CLT based pedagogy: Hyland (2007) claimed that CLT based writing instruction gives importance to collaboration (peer interaction) and scaffolding (teacher-supported learning) thus following modern theories of learning. An important pedagogical conclusion that the findings of this study helped in reaching was that it was observed in this study that the students were learning not only from their teacher but also from each other. They learnt different linguistic conventions and other salient features to benefit from the learning process and enhance their comprehension skills. Peer learning in a pair/group setting showed the lasting effects on the student’s analytical skills in complex situations.
The benefit of Narrative in CLT based pedagogy: The ESL students were not trained to consider the communicative purpose of their writings. The goal of both the teachers and students was to only prepare for the examination that is why they focused on learning rules of grammar through GTM and memorizing model answers. The use of Novel as a source of learning English specifically in ESL classrooms provides a solid platform for CLT based approach to language teaching which emerged in the 1970s that have stressed the role of language in helping learners achieve purposes in a context. The context and social situation provides constraints on the communicative purpose in any kind of genres (Swales, 1990; and Martin1984). It means that a communicative purpose of a piece of writing provides its unique position in a particular genre. The post-test scores of the Experimental group showed how the students wrote better answers because of the treatment that was provided to them for six weeks. It can be stated here that teaching of narrative through CLT based pedagogy improved the communicative aspect of these students’ cognitive learning process. It encouraged them to view writing as a tool that they could utilize, and to understand how writers manage the information from their environment to promote logical organization.
Role of the teacher in CLT-based pedagogy
The findings highlighted the effectiveness of teacher’s role in CLT based approach. The students were provided with guided practice as they developed language skills for meaningful communication. This was particularly beneficial for the struggling students who found it difficult to communicate their thoughts in a coherent manner.
Secondly, this approach encouraged joint effort in communication, in which the teacher and the students participated and communicated a text together. It is extremely important that students learn from a teacher who serves as a more competent person. Teachers and students went through the extensive CLT practices together through joint effort, and shared the responsibility for performance until the students developed their knowledge and skills to write independently.
Conclusion
The experimental nature of this study revealed that CLT based pedagogy was beneficial to low proficient ESL learners in improving their writing skills. The results were consistent with the previous studies conducted by Beretta & Davies, (1985), Swain (1988), Sun & Cheng (2002) and Ahmed & Rao, (2013) who conducted similar studies to test the effectiveness of CLT based approach and reached positive conclusions in their respective studies.
This study not only found certain pedagogical benefits of using CLT based approach but also identified some important pedagogical issues in ESL teaching. The lower percentage of improvement in the students of the control group strengthens the fact that the students rely only on rote learning and cramming could only reproduce what was spoon-fed to them. The traditional method of teaching including lectures based on GTM could only support students in learning the narrative and reproducing it without any cognitive development. On the other hand, students in the experimental group exhibited a better understanding of vocabulary, grammar in their post-test scores and came up with creative sentence structures instead of only reproducing the information from the text. The students of experimental group also displayed an eagerness to accept the appropriately transformed learning process during the CLT based instruction as compared to the students of control group. Moreover, the confidence level of the students in experimental group increased considerably while using the rules of grammar. The students of the control group were not provided with any encouragement to express their own point of view. Consequently, students preferred to look for readymade model answers to questions and memorized them. They did not have the motivation to put in extra effort to write on their own.
It was also observed in this study that the role of the teacher in a CLT based classroom is very crucial. To teach through CLT based approach, the teachers need to not only have a great command over all the salient features of the genre but they should also possess the skills to keep the interest of students high. In this study, explicit contribution by the teacher was involved regarding students’ development of language skills for meaningful communication.
To sum, the study has the potential to help students who struggle with the conventions of English language because of the archaic approaches towards ESL pedagogy in the public-sector institutions in Pakistan. This study has proved how the teachers could help their students by shifting to CLT based instruction without bringing any drastic changes to the syllabus.
References
- Ahmed, S., & Rao, C. (2013). Applying Communicative Approach in teaching English as a Foreign Language: A Case study of Pakistan. Porta Linguarum, 187-203. Retrieved November 2016
- Ahn, H. (2012) Teaching Writing Skills Based on a Genre Approach to L2 Primary School Students: An Action Research. Canadian Centre of Science and Education. 5(2), 2-16. Retrieved From
- Atkinson, D. (2003). L2 Writing in the Post-Process Era: Introduction. Journal of Second Language Writing, 12, 3-15. Retrieved from
- Beretta, A., & Davies, A. (1985). Evaluation of the Bangalore Project. ELT Journal, 39(2), 121-129. Retrieved August 6, 2016
- Canale, M., & Swaine , M. (1980). Theoretical bases of Communicative Approaches to Secong Language Teaching and Testing. Applied Linguistics, 1(1), 1-47. Retrieved October 26, 2016
- Cheng, F. W. (2008). Scaffolding Language, Scaffolding Writing: A Genre Approach to Teaching Narrative Writing. Asian EFL Journal, 10(2). Retrieved from
- Clandinin, D. J., & Connelly, F. M. (1989). Narrative and story in practice and research.
- Ellis, G. (1996). How Culturally Appropriate is the Communicative Approach? ELT Journal, 50(3), 213-218. Retrieved October 26, 2016
- Hyland, K. (2002). Specificity Revisited: how far should we go now? English for Specific Purposes. 21, 385-395. Retrieved from
- Hyland, K. (2003). Genre-based pedagogies: A social response to process. Journal of Second Language Writing, 12(1), 17-29.
- Hyland, K. (2007). Genre Pedagogy: Language, literacy and L2 writing instruction. Journal of Second Language Writing, 16, 148-164. Retrieved from
- Lee, M. W. (2014). Will Ccommunicative Language Teaching work? Teachers' Perceptions towards the new Educational reform in South Korea. Indonesian Journal of Applied Linguistics, 3(2), 1-17. Retrieved August 9, 2016
- Savignon, S. J. (1991). Communicative Language Teaching: State of the Art. TESOL Quarterly, 25(2), 261 - 279. Retrieved August 1, 2016, from
- Sun, G., & Cheng, L. (2002). From Context to Curriculum: A Case Study of Communicative Langage teaching in China. TESL Canada Journal, 19(2). Retrieved August 10, 2016
- Swain, M. (1988). Manupilating and Complementing Content Teaching to Maximize Second Language Learning. TESL Canada Journal, 6(1), 68- 84. Retrieved July 10, 2016
- Temple, C. A., & Gillet, J. W. (1989). Language Arts: Learning Processes and Training Practics. Pearson Scott Foresman.
Cite this article
-
APA : Khan, A. A., Ahmad, H., & Shah, S. R. A. (2016). The Effectiveness of CLT in the ESL Context of Pakistan. Global Language Review, I(I), 85-111. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2016(I-I).08
-
CHICAGO : Khan, Arshad Ali, Hussain Ahmad, and Sayyed Rashid Ali Shah. 2016. "The Effectiveness of CLT in the ESL Context of Pakistan." Global Language Review, I (I): 85-111 doi: 10.31703/glr.2016(I-I).08
-
HARVARD : KHAN, A. A., AHMAD, H. & SHAH, S. R. A. 2016. The Effectiveness of CLT in the ESL Context of Pakistan. Global Language Review, I, 85-111.
-
MHRA : Khan, Arshad Ali, Hussain Ahmad, and Sayyed Rashid Ali Shah. 2016. "The Effectiveness of CLT in the ESL Context of Pakistan." Global Language Review, I: 85-111
-
MLA : Khan, Arshad Ali, Hussain Ahmad, and Sayyed Rashid Ali Shah. "The Effectiveness of CLT in the ESL Context of Pakistan." Global Language Review, I.I (2016): 85-111 Print.
-
OXFORD : Khan, Arshad Ali, Ahmad, Hussain, and Shah, Sayyed Rashid Ali (2016), "The Effectiveness of CLT in the ESL Context of Pakistan", Global Language Review, I (I), 85-111
-
TURABIAN : Khan, Arshad Ali, Hussain Ahmad, and Sayyed Rashid Ali Shah. "The Effectiveness of CLT in the ESL Context of Pakistan." Global Language Review I, no. I (2016): 85-111. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2016(I-I).08