Abstract
This study tests the validity of Dörnyei (2005) L2 Motivational Self System in a new context of Madrassa. A mixed-method approach has been applied in this study. A structured questionnaire was designed and distributed among 1000 students of fifteen different Madrassas of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. The current study posits that the Dörnyei model of the L2 Self System is not valid in the Madrassa context. The study examines that ideal and Ought-to L2 selves are the weakest contributors in motivating Madrassa students for second language learning. The findings reveal no significance among the three main components (ideal self, ought-to self and L2 learning experience) of the L2 Motivational Self System. Moreover, the new construct of learning English for religious purpose was found useful, and all the participants showed their interest in it. This study concluded that multiple personal and religious factors strongly affect the motivational level of Madrassa students.
Key Words
L2 Motivational Self System, Madrassas, Ideal Self, Ought-to Self and L2 Learning Experience
Introduction
This study focuses on the L2 Motivational Self System of Madrassa students at Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. It investigates the lack of motivation, coupled with other multiple socio-economic factors responsible for this aspect of their learning. This research problematizes this issue in order to highlight the reasons behind this mindset. It considers different perception about the English language and culture.
According to Baugh (2003), English is the “lingua franca” of the world, and the reason is that the speakers of this language are highly influential in world politics, science, democracy, and almost all other areas of human life. Thus, in the field of applied linguistics, learning and teaching of the English language is the focal point from various perspectives (Sameer, 2009).
In addition to many other factors, motivation for learning English language plays an important role. Motivation not only fuels learning of the students, but also encourages teachers towards effective language teaching methods. Islam (2013), and Ali (2016) have explored and identified motivation at different levels of education in Pakistan. However, as far as the analysis of the motivation in Madrassa students is concerned, this area seems barren and unexplored to the best of my knowledge and needs to be explored.
The current study focuses on the analysis of L2 motivational Self System of seminaries students in Pakistan. What are the motivational factors that are influencing L2 self of seminary students in Pakistan? How well the Dörnyei L2 does
Motivational Self System fit the data? I have used a mixed-method
(qualitative/quantitative) in the current study. Data has been collected
through questionnaires and semi-structured interviews from different districts
of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP hereafter) in Pakistan. This study aims to explore L2
motivational factors and the validation of Dörnyei's (2009) L2 Self System in the seminary students of Pakistan
during the L2 learning process.
Background of the Study
This
study has been conducted in the backdraft of the different views on the way Madrassa
education is important and why these students shirk from learning the English
language
The purpose of this
section is to describe the geographical location, population, literacy rate,
and socio-linguistic view of Pakistan and its province KP, where the data has
been collected for the current study. These details help in understanding and
explaining the attitude of Pakistani Madrassa students towards English
language learning and the L2 motivation of the participants. Firstly, the
overall linguistic and geographical details of Pakistan in general and then of
KP, in particular, are discussed. Secondly, this section not only explains the
status of English in Pakistani society and its educational system but also
highlights the role and place of English in Madrassas and its recent
inclusion in the curriculum.
Socio-Linguistic Background of
Pakistan
Pakistan
is a multi-cultural and multilingual country. According to Shamim (2011) and
Asher (2008), 72 different languages are spoken in Pakistan. According to the Population
Census Organization (PCO) of Pakistan April 15, 2020), the country has a total
population of almost 200 million, the fifth most populous country in the world,
making up 2.83% of the whole world.). The literacy rate in the country is
43.90%, which is very far below world standards (Ministry of Education, 2009).
According to Capstic (2011), Pakistan spends 2.9% of the budget on education,
one of the lowest in the world. The census of (2001) also revealed that male
literacy figure stood at 55% whereas female literacy figure at 32% in the
country. Almost 65% of people are living in rural areas, and 35.1% are living
in big cities. The female population is 48% in Pakistan, according to the
latest census conducted in (1998) and published in (2001).
The country has four provinces,
Punjab, Sindh, KP and Baluchistan); two autonomous provinces (Azad Jammu and
Kashmir, Gilgit Baltistan) and the federal territory (FATA) also the capital of
Pakistan, Islamabad. According to Rehman (2003, 2007), a huge population of the
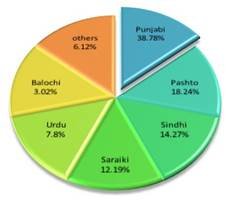
country (almost 96%) speak the regional languages, Punjabi, Pashto, Sindhi, Saraiki,
Urdu, and Balochi, as their native language. Punjabi and Saraiki have mutually
understood languages of the Punjab province, which is the most populous
province of Pakistan, 56.3% of the whole population. Pashto, Balochi, and
Sindhi are spoken in the other provinces of the country. Urdu, the national
language of the country, has a limited number of native speakers and is
understood in all parts of the country (Mansoor, 2004). According to the (Census 2017), the
six major languages can be seen in the following table.
Table 1. The Linguistic Profile of Pakistan
|
Main Languages |
Speakers Percentage |
Regions |
Status |
|
Punjabi |
38.78% |
Punjab |
Regional |
|
Pashto |
18.24% |
KP and Ex FATA |
Regional |
|
Sindhi |
14.27% |
Sindh |
Regional |
|
Saraiki |
12.19% |
Southern Punjab |
Regional |
|
Urdu |
7.8% |
Urban Sindh and some parts of Punjab |
Regional |
|
Baluchi |
3.02% |
Baluchistan |
Regional |
|
Others |
6.12% |
Different parts of Pakistan |
Local |
Pashto is the second-highest language spoken in the
country, as shown in the pie chart on the next page.
Significance of the Study
This study is an addition to the area of English language teaching (ELT). The study also shows the positive side of Pakistani Madrassas by adding English subjects to their curriculum. After the incident of 9/11, such places were only known as the terrorist’s hubs in the world and mainstream media (Rehman, 2007). This study also incorporates the common hypothesis of Pakistani education policymakers that the Madrassas education system does not welcome secular education in general and the English language in particular.
This study is important to bring harmony to the education system of the country, and all institutions should practice an education system that should be acceptable to all type of schools. The study also plays the role of bridging Madrassa and universities students as the study revealed that due to better proficiency in the English language, university students consider Madrassa students inferior in education.
Literature Review
Motivation
Motivation is a juxtaposition of factors that stimulate human actions; motivation stimulates people to think and behave. According to Dörnyei (2006), motivation is concerned with
“The direction and magnitude of human actions, that is, the choice of a particular action, the persistence with it and the effort expended on it”.
Motivation emanates from ambition or aspiration, which later on counsel human actions. Motivation is difficult to define as it does not only contain alternatives, instructions, and continuance of human conduct but also has manifold arguments behind all these aspects. The multidimensional nature and the broad range of motives for human conduct make it hard to elaborate a universal and ''an integrative 'super theory of motivation''. This is the reason that investigators must concretize their concentration on its unidentified aspects while theorizing it (Dörnyei and Ushioda, 2011). Here, I will attempt to define the idea of motivation (in terms of L2 context) with the assistance of several interpretations offered by other researchers.
The success and failure of a second language learner are determined by the level of motivation he has. In most cases, motivation is related to one’s intentions, enthusiasm, and thirst for doing-or achieving something. It is not easy to explain the term ‘motivation’ in a single line definition because its definition varies from person to person. It is interesting to note that what motivates one person may not motivate others (Hadfield, 2013). I am going to discuss some well-known definitions of motivation by different dictionaries and experts.
The Oxford Online Dictionary (2014) describes the term motivation as a desire or willingness to do something.
Cambridge Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (4th edition) explains motivation as enthusiasm for doing something or the need or reason for doing something.
Macmillan Dictionary illustrates the term motivation as a feeling of enthusiasm or interest that makes you determined to do something.
Motivation being a mind-related phenomenon has also been defined by psychologists as well. M. David (1991) defines motivation as the ‘reason(s) by which a person starts the activities or the process through which activity is directed and sustained in a certain period so that one should meet his/her needs. Such needs can be physical as the need for food or psychological as the need for validation. Psychologists have proposed many theories dealing with different aspects of motivation. Some of these theories talk about need and others about arousal and instinct. The Dictionary of Psychology (2012) defines motivation as:
It is a driving force that sets a direction to the human or animal behavior at conscious or unconscious level” or “A level of willingness that a person has for achieving his goals, a level can be physical or mental.
Dörnyei and Hadfield (2013) consider teachers’ role extremely important in developing students’ motivation towards learning. Maintaining the students’ motivation throughout the semester is one of the most challenging tasks for teachers. Burden and Williams (1997) are of the view that motivation is a kind of mental activation/force that gives power to a person (physical or mental) to achieve his goals. Motivation not only plays a role in a man’s social life, but it also plays a vital role in successful educational. Hunts and Wiseman (2008) describe motivation as the inner urge that is aroused in a person at certain times who has the aim of achieving something. That urge may have a huge impact (positive/negative) on human conduct when it comes to achieving his goals.
Pintrich (2003) considers motivation a very complex term. He believes that it is almost impossible to find out why someone is doing something as the reasons behind that action can vary over time. He further adds that motivation is divided into two types, intrinsic and extrinsic, and it is not easy to ascertain which kind is forcing students to learn or get an education. He further says we often cannot be sure which type of ‘motivation’ is at work because most of the time, both types of motivation are at work behind a person achieving something. In line with this argument Pintrich (2003) has given four dimensions that contribute to motivation:
1. Competence: Are the students capable of completing a task?
2. Autonomy/control: How will students control a given task? It creates a direct link between their actions and the outcomes.
3. Interest: Is the task interesting for the students? Is the effort worth making?
4. Relatedness: What would be the reaction of others? Will he get any approval from his/her classmates or from society?
These four dimensions are drawn from the works of many other scholars as well. V, Eskja (2017), in his article “The Impact of Motivation in an Educational Environment”, explains the positive side of motivation in education and the negative effects of demotivation in the same environment. He has defined how to bridge the internal and external motivational factors together. He also throws light on how to bridge the gap between teachers and students in the academic and educational environment. He further explains the role of a teacher as a motivator so much so that he would always encourage his students; he should have a dynamic and vivacious personality and should work on the positive attitude of the students. He further stresses the bridging of the communication gap between teachers and students, which is a hindrance to the motivation of students and their learning process. His study is based on the theories of Herzberg (1964), Maslow (1943), and McClelland (1957).
Eskja (2017) says that time has changed. Technology has replaced many old things; teaching methods are one of them. He urges pedagogues to pay special attention to the adaptation of motivation in learning. He supports William (2011), five entities that are influencing students’ motivation level and plays a vital role in the L2 learning process they are teacher, student, method, content, and environment. He quoted Palmer (2007) as saying that quality education is only possible when you motivate your students. Teachers should monitor and evaluate students’ motivation throughout the academic year. When your students ask more and more questions, do their assigned tasks enthusiastically and are eager to learn more and more, these are the signs which show that your students are motivated to learn.
L2 Motivation Self System
The idea of the L2 Motivation Self System Stage (L2MSS) was proposed by (Dörnyei 2005). L2 motivation Self System judges L2 learners on three different levels;
1. The ideal self is when a learner wants to speak a second language; he likes English for the sake of English, and he carries an image or portrait of his ideal person that he wants to become. Dörnyei explains the ideal self as “the L2 specific facet of one’s ideal self”.
2. Ought-to L2-self is “the attributes that one believes one ought to possess? For example, responsibilities, obligations, and various duties to avoid possible negative outcomes from the people or family and friends”. The learner tries to do his best, possibly not because he loves the language but because he loves his family and wants to take care of it. He tries to avoid any possible negativity in the future by not getting good marks in English.
3. The learning experience is the last element of L2MSS. Second language learning experience refers to “situational specific motives related to the immediate learning environment and experience”.
Overview of the Studies Conducted on Learners’ L2 Motivational Self
L2 motivation Self System has been tested in many countries such as Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Hungary, China, Japan, and Iran (Islam, 2013; Al-Shehri; Ryan 2009; Taguchi, Magid, and Papi 2009) for its validation. In the coming lines, I am going to discuss some of the relevant studies briefly.
Islam (2013) has researched Dörnyei's L2 motivation Self System system in Pakistani universities. The topic of his study was “L2 Motivation Self System and Relational Factors Affecting the L2 Motivation of Pakistani Students in the Public Universities of Central Punjab, Pakistan". Islam's thesis presents the motivation level of Pakistani undergraduate students for the English language by using the L2MSS of Dörnyei (2009).
The aim of the study was twofold; firstly, to check the usefulness of Dörnyei's presented Self System of L2 motivation in the Pakistani context, and secondly, to find other related factors for boosting motivation in the second language process. He distributed 1000 questionnaires in undergraduate students of seven public sector universities in Punjab. Mix method approach was adopted for the said study. The study got noteworthy results and support in terms of validating the L2 system in the Pakistani context. The students’ high motivation for the English language has been shown in both qualitative and quantitative results. In the qualitative section, "I will learn English till death", the type of responses was noted that shows how much students were motivated for L2 learning (Islam, 2013).
Milieus had a huge role in the L2 motivation of the students and influenced the future self of the students in that study. Islam (2013) urges scholars to explore this theory of L2MSS more in the Pakistani context. Islam (2013) has constructed the new concept of National Interest in the study as well; the theme of the construct is how students can play an important role in the economic development of the country with a promising performance in the English language.
Research Questions
This study had many research questions. However, in this paper, the researcher focused on addressing only the following major research questions:
1. What are the motivational factors influencing the L2 self of the seminary students in Pakistan?
2. How well does the Dörnyei L2 motivational Self System fit the data?
Methodological Structure of the Study
To explain and
examine the L2 motivation of the Madrassa students, the researcher has
adopted a mixed method approach in the current study. In this regard, the L2
motivation of seminary students has been tested using the lens of L2MSS and
other motivational factors in the L2 learning process. The researcher has added
10 questions to the structured questionnaire at the end of the chapter (purely
related to learning English for religious purposes). Both qualitative and quantitative approaches
have been adopted for data collection and analysis in this study (mixed
method).
In the typology of mixed-method
research design, this research falls in the category of ‘partially mixed
concurrent dominant status design’. This typology of the mixed method is given
by Leech (2007). In this category, both approaches, qualitative and
quantitative, happened at the same time, and one of them, the quantitative, in
the case of this study, has got more emphasis than qualitative (Leech, 2009).
Selection of the Sample
The
researcher has selected the last four Darjas (classes) for this study as
they are senior and mature. Zenter (2007) claims that a suitable vision for the
future self does not develop in childhood. I selected KHAMISA (GRADE 5),
SADISA (GRADE 6), SABIA (GRADE 7), and SAMINA (GRADE 8)
for the current study.
Description
of the Sample of this Study
Overall,
1000 questionnaires (almost 62 in each Madrassa) were distributed among
the students of fifteen Madrassas. I received positive responses from (93%)
students by receiving 933 filled questionnaires. I omitted the incomplete
questionnaires or the questionnaires filled in a careless manner.
Table 2. Background
Information of the Students
|
Details |
Sample |
Percentage |
|
Sample |
933 |
93.3% |
|
Gender |
|
|
|
M |
776 |
83.17 |
|
F Year of Study 5th (Khamisa) 6th (Sadisa) 7th (Sabia) 8th (Samina/Alia) |
157
131 157 247 398 |
16.82
14.0 16.8 26.4 42.6 |
Table 1 shows a huge gender diversity where only 16%
of the sample is female. It was a hard task to collect data from female (BANAAT)
Madrassas students due to their strict religious (parda)
obligation.
Table 3. District
Wise Distribution of the KP for Collecting Data
|
Southern Areas |
Central Areas |
Northern Areas |
|
Banu |
Peshawar (F) |
Malakand |
|
Karak |
Mardan (F) |
Dir |
|
Hangu |
Charsada (F) |
Swat |
|
Kohat |
Sawabi (F) |
Mansehra |
|
|
Nowshehra (F) |
|
(Note) “F” indicates female Madrassa
The whole province has been divided into three parts
southern, central, and northern. Secondly, one Madrassa from each district has
been selected for the data collection process, including two EX-FATA areas.
Female Madrassas were affiliated with the boy’s Madrassas;
however, their sections were separate.
Data
Collection Tools
Two
tools used for data collection were structured questionnaires and
semi-structured interviews.
Structured
Questionnaire
A structured questionnaire was used for collecting
quantitative data. The purpose of the questionnaire was to find the L2
motivation factors in Madrassa students. Islam (2013) has developed a new concept of national interest as a
future self. I also included that for Madrassa students by adapting his
questions.
Ten questions were added in the last portion of the
questionnaire, purely based on learning English for serving religion
(motivation factor) in a better way, domestically, nationally, and
internationally. Some questions were deleted; for example, “Do you like
watching English movies" as such questions were useless in the Madrassa
context because they consider watching movies an unIslamic act. (Shaikh
Muhammad Ahmad Ismael 2006).
The Procedure of Quantitative Data Analysis
While
analyzing quantitative data, I kept a few things in mind. Firstly, it was noted
that either motivational factors are the same for male and female students, or they
can be different in both genders. For that purpose, the data were analyzed in
two stages; first, the overall tabulation was completed through SPSS 20.0
software, and secondly, the gender-wise analysis was made through the same
software. Secondly, the entire tables were described in detail with the
motivational factors which are different for male and female students.
Furthermore, Dörnyei (2007) L2 Motivational
Self System has been observed in the overall analysis. It has kept been in mind
that either this system exists in the second language learning process or not.
Fourthly, the new construct ‘learning English for religious purposes has been
highlighted with more details.
Results and Analysis
Reliability
Analysis of the Questionnaire
To find out the reliability of all
scales of the questionnaire, another test was conducted for this purpose after
entering data into SPSS (V20). In this regard, Cronbach Alpha Coefficients were
calculated with the help of SPSS software.
Two scales (National Interest and
Religious Interest) have more than .7 alpha values which are highly acceptable
in social science studies and other studies conducted on L2 motivation.
Furthermore, six scales (Ideal L2 self, ought to L2 self, English anxiety,
instrumentality-prevention, Instrumentality-promotion, and International
posture) have alpha value close to .7, which also has a satisfactory inter-item
correlation. The scale of 'Religious Interest' has the highest value of .81,
which shows the interest of the sample for learning English to serve Islamic
religion, which is further explained in the interview section.
Table 4. Scales
Reliability Test in the Questionnaire
|
S. No |
Scales |
No. of Items |
Cronbach Alpha |
Mean Interitem Correlation |
|
1 |
Ideal L2 self |
8 |
.63 |
.20 |
|
2 |
Ought-to L2 self |
6 |
.67 |
.28 |
|
3 |
Attitudes to Learning English |
3 |
.60 |
.31 |
|
4 |
Attitude towards L2 Community |
6 |
.58 |
.22 |
|
5 |
Cultural Interest |
2 |
.50 |
.14 |
|
6 |
English Anxiety |
4 |
.68 |
.29 |
|
7 |
Intended Learning Efforts |
6 |
.62 |
.18 |
|
8 |
Instrumentality – prevention |
5 |
.66 |
.23 |
|
9 |
Instrumentality – promotion |
7 |
.69 |
.26 |
|
10 |
Integrativeness |
3 |
.28 |
.10 |
|
11 |
International Posture |
8 |
.67 |
.32 |
|
12 |
National Interest |
5 |
.71 |
.43 |
|
13 |
Milieu |
6 |
.59 |
.21 |
|
14 |
Religious Interest |
10 |
.81 |
.40 |
I have excluded integrativeness from
further analysis, which scored the lowest alpha value of .28 and meant
inter-item of .10. In this case, the values are very low to measure the L2
motivation of the present sample. Unlike Islam (2013), the scale of Ought to L2
self has not very high alpha value (only .67) and inter-item correlation (.28)
which is in line with the (Lukacs 2010) and (Csizer 2008) studies. It has been
included for the analysis despite its low values as it plays an important role
in measuring the L2 motivation or demotivation of the sample. Apart from that,
instrumentality promotion and instrumentality prevention scored good alpha
values, corresponding with the results of Taguchi (2009), which are kept for
further analysis.
Motivation Factors
Table 5. L2
Motivation Factors for Madrassa Students
|
Factors |
N |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Mean |
|
Cultural
Interest |
933 |
1.00 |
6.00 |
3.77 |
|
Attitudes
towards L2 Community |
933 |
1.17 |
5.67 |
3.55 |
|
Instrumentality
(Promotion) |
933 |
1.26 |
5.80 |
3.50 |
|
Instrumentality
(Prevention) |
933 |
1.00 |
5.80 |
3.37 |
|
International
Posture |
933 |
2.00 |
5.67 |
3.96 |
|
English
Anxiety |
933 |
1.25 |
5.50 |
3.49 |
|
Attitudes
towards Learning English |
933 |
1.00 |
6.00 |
3.29 |
|
Milieu |
933 |
1.17 |
5.67 |
3.40 |
|
Ideal L2 Self |
933 |
1.25 |
5.75 |
3.35 |
|
Ought-To L2
Self |
933 |
1.00 |
5.24 |
2.51 |
|
Intended
Learning Efforts |
933 |
1.00 |
5.50 |
3.43 |
|
National
Development |
933 |
1.20 |
6.00 |
4.06 |
|
English
Learning for Serving Religion |
933 |
3.10 |
5.90 |
4.82 |
Note 1:
As the Likert scale consists of 1-06 scales, so the
average or mean is (1+2+3+4+5+6)/6=3.5.
Thus, the factors whose mean/average score is above
3.5 are the motivating factors and vice versa.
Here in this table, all the blue highlighted
factors are the motivating factors; make sure that all the statements are of
reverse order.
Note 2:
On the Likert scale of two
points, that is 1 and 2; their a mean score is above 1.5; then it shows that
females are more motivated than male and if it is below 1.5 then males are more
motivated than female. In this case, males are more motivated as compared to
females.
The L2 future selves of Madrassa students have
been influenced by different motivational factors to learn English which has
been explained in this section. The most prominent of which is learning English
for religious purposes that dominated other motivational factors in the Madrassa
setup. The basic objective behind learning English was to spread Islam in the entire
world; more than 90% showed their keen interest in it.
Regression
Model Based on Ideal L2 Self, Ought to L2 Self, Attitude to Learning English
and Learning English for Serving Religion as a Criterion Measure
Table 6. Religious Interest and L2 Self System
|
Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R
Square |
Std. The
error of the Estimate |
|
1 |
.410a |
.168 |
.166 |
.67952 |
a. Predictors: (Constant), ATTITUDES TO LEARNING
ENGLISH, OUGHT-TO L2 SELF, IDEAL L2 SELF
The above model shows R square of 0.168, which shows
explains that 16.8% variation in the response variables is explained by the
independent variables considered in the study.
Table 7. ANOVAa
|
Model |
Sum of Squares |
Df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
|
|
Regression |
86.864 |
3 |
28.955 |
62.707 |
.000b |
|
Residual |
428.965 |
929 |
.462 |
|
|
|
|
Total |
515.829 |
932 |
|
|
|
|
a. Dependent Variable: ENGLISH LEARNING FOR SERVING
RELIGION
b. Predictors: (Constant), ATTITUDES TO
LEARNING ENGLISH, OUGHT-TO L2 SELF, IDEAL L2 SELF
Table 8. Coefficients
|
Model |
Unstandardized
Coefficients |
Standardized
Coefficients |
T |
Sig. |
Collinearity
Statistics |
||
|
B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
Tolerance |
VIF |
|||
|
(Constant) |
3.987 |
.085 |
|
47.100 |
.000 |
|
|
|
Ideal L2 self |
.050 |
.062 |
.054 |
.801 |
.424 |
.456 |
2.193 |
|
Ought-to L2 self |
-.020 |
.012 |
-.223 |
-1.575 |
.127 |
.705 |
1.419 |
|
Attitudes to learning English |
.189 |
.026 |
.292 |
7.282 |
.000 |
.557 |
1.794 |
a. Dependent Variable: ENGLISH LEARNING FOR SERVING
RELIGION
The above tables explain that the model is
statistically significant with a p-value .000. In the table having coefficients
of independent variables in the model, the results portray that attitude to
learning English is significant, with a 1 percent level of significance. Apart
from that, ideal L2 self and ought to L2 self is insignificant to the dependent
variable English learning for serving religion. These results are further
supported by the qualitative data frequencies and elaborated under the
quantitative data.
Findings of Qualitative Data
This chapter has provided important findings of qualitative data.
This chapter has provided the fact that the core motivation for learning English at Madrassas is to spread the Islamic religion throughout the world. None of the thirty participants showed any type of disagreement with the questions asked in this regard.
This chapter has presented the attitude of Madrassa students towards the culture of the L2 community and L2 speakers. Surprisingly, all thirty participants showed a negative attitude towards English culture.
Conclusion
Research Questions and their Findings
The current study was based on four main questions. In this paper, I have taken only two.
Question one was
1. What are the motivational factors influencing the L2 self of the seminary students in Pakistan?
In response to the above question, it has been revealed that the motivational factors that are influencing L2 self of the seminary students in KP, Pakistan are: English learning for serving religion, national development, culture interest, attitude towards L2 community, instrumentality (promotion), international posture and intended learning efforts.
Question two was
2. How well does the Dörnyei L2 motivational Self System fit the data?
The finding for this question has shown that the L2 motivational Self System of Dörnyei does not fit the data in all aspects. This has been examined in qualitative and quantitative data that ideal and ought-to L2 selves are the weakest contributors in motivating Madrassa students for second language learning.
References
- Aznar. (2003).The Negligible Role of Government in the Development of Pakistani Madrassa, a Sad Perspective. Kareem Printers Pakistan
- Barnette. (1941). The Palace Schools of Mullammad the Conqueror, Harvard University Press, Cambridge
- Baugh, A. C. (2003). A History of the English Language Fifth Edition, British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library
- Coleman, H. (2010) Teaching and Learning in Pakistan: The Role of Language in Education. Islamabad: The British Council.
- Dörnyei, Z. (2005). The psychology of the language learner: individual differences in second language acquisition, Published by Routledge.
- Higgins, E. T. (2013). Beyond Pleasure and Pain. American Psychologist, 52, 1280- 1300. HIGGINS, E. T. 1998. Promotion and prevention: Regulatory focus as a motivational principle. Advances in experimental social psychology, 30, 1- 46.
- Islam, M. (2013). L2 motivational Self System and relational factors affecting the L2 motivation of Pakistani students in the public universities of Central Punjab, Pakistan. Unpublished PhD dissertation. University of Leeds, Leeds. Retrieved from
- Mansoor, A. (2016). Motivations and attitudes towards learning English in Pakistan: A mixed-methods study of urban-rural postgraduate learners' motivations and attitudes towards studying English at a public university in the KP province.
- Mehfooz, F. (2016). Halat e Hazira aur Ulima e Haq ki Zimadariyaan. Hafiz Printers Pakistan
- Miller, J. G. & Schaberg, L. (1941). Cultural Perspectives on Personality and Social Psychology. In: MILLON, T., LERNER, M. J. & WEINER, I. B. (eds.) Handbook of Psychology, Personality and Social Psychology. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons
- Qasim, M. (2000). Barsagheer Pak o Hind Main Ulima ka Kirdar. Hafiz Printers Pakistan
- Qasim, M. (2014). Ulima e Deoband ka Tarekhi Pasmanzer. Hafiz Printers Pakistan.
- Rahman, T. (2007). The Role of English in Pakistan With Special Reference to Tolerance and Militancy. In: AMY B. M. TSUI & JAMES W. TOLLEFSON, E. (ed.) Language Policy, Culture, and Identity in Asian Contexts. New York: Routledge.
- Sameer. (2009). Role of L2 Motivation and the Performance of Intermediate Students in The English (L2) Exams in Pakistan. LANGUAGE IN INDIA, 10, 37 - 49.
- Schmitt, N. (2002). An introduction to applied linguistics., London, Arnold
- Shah, M. A. (1997). The foreign policy of Pakistan: ethnic impacts on diplomacy, 1971-1994, London, I B Tauris & Co Ltd. Author. 2010. 26 languages spoken in NWFP, northern areas: Many face threats of extinction. Daily Times.
Cite this article
-
APA : Shah, S. A. A., Khan, A. H., & Samad, A. (2020). L2 Motivational Self System of the Seminary Students learning English Language in Pakistan. Global Language Review, V(IV), 54-64. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2020(V-IV).07
-
CHICAGO : Shah, Syed Azaz Ali, Abdul Hamid Khan, and Abdus Samad. 2020. "L2 Motivational Self System of the Seminary Students learning English Language in Pakistan." Global Language Review, V (IV): 54-64 doi: 10.31703/glr.2020(V-IV).07
-
HARVARD : SHAH, S. A. A., KHAN, A. H. & SAMAD, A. 2020. L2 Motivational Self System of the Seminary Students learning English Language in Pakistan. Global Language Review, V, 54-64.
-
MHRA : Shah, Syed Azaz Ali, Abdul Hamid Khan, and Abdus Samad. 2020. "L2 Motivational Self System of the Seminary Students learning English Language in Pakistan." Global Language Review, V: 54-64
-
MLA : Shah, Syed Azaz Ali, Abdul Hamid Khan, and Abdus Samad. "L2 Motivational Self System of the Seminary Students learning English Language in Pakistan." Global Language Review, V.IV (2020): 54-64 Print.
-
OXFORD : Shah, Syed Azaz Ali, Khan, Abdul Hamid, and Samad, Abdus (2020), "L2 Motivational Self System of the Seminary Students learning English Language in Pakistan", Global Language Review, V (IV), 54-64
-
TURABIAN : Shah, Syed Azaz Ali, Abdul Hamid Khan, and Abdus Samad. "L2 Motivational Self System of the Seminary Students learning English Language in Pakistan." Global Language Review V, no. IV (2020): 54-64. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2020(V-IV).07