Abstract
Aligning assessment practices with instructional and learning strategies trigger deep learning. However, research confirms that some language teaching contexts do not moderate a positive association between assessment methods and course learning outcomes (CLOs). This research attempted to examine the congruence between assessment task designs and CLOs of an English-major program in a Saudi public university and evaluate the authenticity of the tasks. To seek answers for the research questions, final examination marked papers of nine randomly selected courses were evaluated. The study used a documentary research method. The question papers underwent both quantitative and qualitative analysis. The results evinced inconsistencies in assessment task designing and marking styles across the courses. The tasks were invalid and unauthentic, and they did not match CLOs. Therefore, suggestions are presented that the assessment practices should be revisited to stop assessment tempering in the interest of observable and sustainable academic achievements.
Key Words
Assessment Tasks, Authenticity, Critical Thinking, Learning Outcomes, Quality Assurance
Introduction
This article reports a documentary analysis of the validity of summative examination assessment tasks of nine English major courses of a Saudi pubic university. In order to make valid inferences from the assessment of students’ learning outcomes, it is imperative that assessment instruments are valid and reliable. Valid and reliable assessment of students’ learning outcomes is necessary for institutions, learners and society alike. It has been observed that most Saudi students get grades that are untrue of their actual academic achievements. One of the reasons behind this problem is a mismatch between CLOs and the assessment tasks. Therefore, this study evaluated the nature of end-of-course examinations given to English major students as a major part of the assessment. Thus, this study though very limited in scope carries immense significance to highlight assessment methods that obstruct the fulfillment of higher-order learning.
Literature Review
The Validity of Assessment Tasks
Valid assessment tools measure exactly what they are required to measure (Coombe and Evans, 2005) whereas invalid tests usually concede false inferences regarding students' achievement. Therefore, it is imperative for a language assessment task to show the actual achievement of learners otherwise the results are deceptive. Learners get commendable scores (certificates) without having achieved the intended learning outcomes (Green, 2007b). Therefore, Green (2007a) has given the model of overlap that asks for maximum overlap between exam specifications and the target academic and linguistic skills intended to be achieved (see Figure 1). The greater the overlap the greater is the achievement of learning outcomes.
Figure 1
A Model of Washback Direction (Green, 2007a)
Every educational program or course has certain learning outcomes that its learners are trained to achieve (Archbald and Newmann, 1988). To ensure the successful achievement of the learning outcomes, there is a need to examine the progress of learning. This aim can only be achieved by employing valid assessment tasks that are ‘worthwhile, significant, and meaningful—in short, authentic’ (Archbald and Newmann 1988, p.1). Such authentic assessment tasks require the production of new knowledge or applying concepts to novel situations rather than a mere reproduction of previously taught information (Muñoz and Álvarez, 2010). They have remarked that it is easy for teachers to decide if “students have a real understanding of the material presented and they are able to synthesize concepts” (2010, 44). However, the situation according to them can be different if the assessment tasks lack authenticity and have a strong similarity to teaching tasks. These causes make students memorize selected materials and resultantly teachers cannot determine the actual acquisition of the concepts and skills.
Previous Studies
A critical review of previous studies suggests that valid and authentic tests have mostly resulted in the achievement high-order learning (Muñoz and Álvarez, 2010; Benedetti, 2006; Saif, 2006; Ferman, 2004; Manjarrés, 2005; Stecher, Chun and Sheila, 2004; Cheng, 1997). For example, it has been noted that listening tests based on video are more reliable than their audio counterparts (Benedetti, 2006). The fusion of oral elements in end of school assessment had a beneficial impact on Matriculation students’ oral proficiency compared to pen and paper examination (Ferman, 2004). The study of Saif (2006) revealed that a strong alignment between test specifications and course learning outcomes generates observable positive washback. This was confirmed by Stecher, et al. (2004) in their study of reforms introduced to the assessment regime of the writing component of examinations in Washington State where changes in assessment tools showed a considerable positive impact on learning processes. In addition, the studies of Manjarrés (2005) and Muñoz and Álvarez (2010) also confirm the argument that a strong correlation between course learning outcomes and test specifications has a beneficial effect on both teaching and learning.
It has to be born in mind that the alignment itself may not yield expected results. Therefore, it is mandatory to apprise students regarding how to access assessment tasks. This argument is supported by the findings of Cheng (1997). It was found in the study that despite the assessment tasks being aligned with course learning outcomes students’ learning did not show the expected positive evidence. Therefore, teachers’ role becomes critical along with decision-makers or supervisors.
Invalid and unauthentic assessment tasks, however, are surely a major cause of lower-order and superficial learning as confirmed by empirical evidence in different settings (see for example Scouller, 1998; El-Ebyary, 2009; Gijbles, Segers and Struyf 2008; and Gijbels and Dochy, 2006). The findings of these studies show that students focus only on lexical and grammatical accuracy because assessment task designs are contrary to learning outcomes. Some assessment tasks even only measure lower order language skills (Gijbles, et al., 2008). Consequently, learners do not tend to focus on improving higher-order cognitive skills (Gijbels and Dochy, 2006). One example of such assessment tasks are multiple choice questions that mostly cause surface level learning (Scouller, 1998). From the two categories of studies with positive and negative washback, we can infer that strong congruence between assessment instruments and the outcomes of a course is indispensable else the entire exercise of education can pale into insignificance.
Methodology
Based on the analysis of the tasks, two categories were formulated, i.e., SROs and CROs (see Table 1&2). The data analysis yielded very straight forward results. More than two-thirds of the tasks were SROs. The CROs were given mainly in literature exams. All linguistics and skill courses except Morphology were SRQs. Moreover, three-fourth of the total marks were allotted to the SRQs.
Table 2. Marks distribution for CROs
|
|
Course
Name |
SRQs |
CRQs |
Total Marks |
||
|
|
|
No of Tasks |
Marks |
No of Tasks |
Marks |
|
|
1 |
Morphology |
6 |
54 |
2 |
06 |
60 |
|
2 |
Modern
English Drama |
0 |
00 |
4 |
60 |
60 |
|
3 |
Nineteenth
Century Novel |
3 |
30 |
1 |
30 |
60 |
|
4 |
Modern
Poetry |
1 |
21 |
3 |
39 |
60 |
|
|
Course |
No of tasks |
Marks |
Space
provided (number of lines) |
|
1 |
Morphology |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
2 |
3 |
2 |
||
|
2 |
Modern
English Drama |
1 |
15 |
5 |
|
2 |
15 |
23 |
||
|
3 |
15 |
21 |
||
|
4 |
15 |
5 |
||
|
3 |
Nineteenth
Century Novel |
1 |
30 (4
topics) |
4 |
|
4 |
Modern
Poetry |
1 |
13 |
9 |
|
2 |
13 |
10 |
||
|
3 |
13 |
8 |
||
|
|
Average
No of lines per question |
13 |
10.38 |
8.9 |
|
|
St.
Deviation |
|
|
7.4 |
Table
4 has the most significant results of the research. No obvious match was noticed
between task designs and the intended course-learning outcomes. Most of the
outcomes were not assessed at all. Surprisingly four of the courses i.e.,
Poetry, Drama IELTS, and Paragraph Writing assessed none of the learning
outcomes. Assessment tasks of other courses such as Phonetics and Semantics
measured just one of the formulated outcomes. The only exam that measured most
outcomes was Modern Poetry.
Table 4. The overlap between
task designs and CLOs
|
Course
Name |
No of Tasks |
No of CLOs |
No of CLOs covered |
No of CLOs
not covered |
|
Situational English |
6 |
6 |
2 |
4 |
|
IELTS |
2 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
|
Paragraph
Writing |
5 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
|
Phonetics |
2 |
5 |
1 |
4 |
|
Semantics |
6 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
|
Morphology |
6 |
5 |
2 |
3 |
|
Modern
English Drama |
4 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
|
Nineteenth
Century Novel |
3 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
|
Modern
Poetry |
10 |
10 |
6 |
4 |
|
|
12 (28%) |
25 (68%) |
||
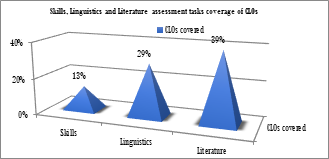
Figure 2
Skill Courses Assessment Tasks Mapped Against the CLOs
|
|
Course
Name |
Instructor
Qualification |
Number of
Tasks |
Total No. of
CLOs |
Number of
CLOs covered |
Number of
CLOs not covered |
|
1 |
Modern
English Drama |
PhD |
4 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
|
2 |
IELTS |
PhD |
2 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
|
3 |
Paragraph
Writing |
PhD |
5 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
|
4 |
Phonetics |
PhD |
2 |
5 |
1 |
4 |
|
5 |
Semantics |
PhD |
6 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
|
6 |
Morphology |
PhD |
6 |
5 |
2 |
3 |
|
Percentage of CLOs covered |
25 |
25(100%) |
4(16%) |
21 (84%) |
||
|
7 |
Situational English |
MA |
6 |
6 |
2 |
4 |
|
8 |
Nineteenth
Century Novel |
MA |
3 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
|
9 |
Modern
Poetry |
MA |
10 |
9 |
5 |
5 |
|
Percentage of CLOs covered |
19 |
17 (100%) |
7(41%) |
9 (59%) |
||
Figure 3
Coverage of CLOs by all assessment tasks of all domains
Discussion
The study focused on three areas i.e., validity and authenticity of the assessment tasks and the level of consistency across different courses. The first research question sought to examine if the tasks assessed the intended learning outcomes. The findings indicated that three-fourth (68%) of the outcomes were not measured that referred to validity issues in the assessment regime across the whole program. Interestingly four of the courses (see Appendix A) did not assess any of the intended learning outcomes. The most interesting dimension of this point is the skill course assessment tasks. It is mandatory for such course examinations to assess the target skills. However, as the findings showed, apart from situational English none of the skill courses assessed any of the learning outcomes provided in the approved course specifications. As noted in the literature review, for assessment tasks to be instrumental in assurance of quality learning they have to be an explicit alignment with the course learning outcomes because assessment is not separate from teaching and learning processes; they are intimate and linked together (Frankland, 2007; Boud, Cohen & Sampson, 2001). Learners are stakeholders in assessment practices (Saville and Hawkey, 2004). Their perception of a test shapes their learning styles. Assessment tasks not covering course learning outcomes will concede superficial learning (El-Ebyary, 2009; Gijbles, Segers and Struyf, 2008; Gijbels and Dochy, 2006; Scouller, 1998). On the other hand, empirical evidence indicates modifying test specifications influence teaching and learning (Saif, 2006; Ferman, 2004). Therefore, based on the findings of previous research it is safely posited that the assessment task designing in the context of this study needs alignment with course learning outcomes to develop higher-order learning.
The second research question required an evaluation of the authenticity of the assessment tasks and the anticipated validity of the inferences drawn from students’ actual performance on the given tasks. The authenticity factor requires assessment tasks to resemble real-life-like performance (Green, 2006; Messick, 1996, and Archbald and Newmann, 1988). The findings showed that none of the assessment tasks were truly authentic in nature. The learning outcomes of courses such as Situational English, IELTS and Paragraph Writing should be assessed through tasks that can reflect students’ achievement of the skills instead of using SRQs tests which only show students’ knowledge. Thus higher-order cognitive, as well as interpersonal skills, remain untested. Therefore, any inferences drawn from students’ results on such a test cannot be reliable. Similarly, the CRQs do not make learners think critically, analyze, synthesis and evaluate information. The CRQs given in examinations seemed to require the reproduction of limited and memorized information.
Regarding the last research question, it was noted that almost three-fourth of the assessment tasks were SRQs. Five of the courses did not have any CRQs. In addition, the findings revealed vivid inconsistency in marks allocation and the space provided to be used by students for answering CRQs. For example, as shown in Tables 3 and 4, marks were allocated for two-line answers whereas five-line answers carried 15 marks. It should be made clear at this point that the students seemed to have an implicit but very strong message that they should use the allotted space only, i.e., no need for using extra space. Last but not the least data analysis revealed that most of the CRQs were short answers memorized by students with great resemblance to answers across whole classes. However, at the same time, it was found that all instructors-cum-examiners had an identical approach to assessment task designing. Almost all of them design SRQs and short answer questions. This may be due to an undeclared departmental policy towards assessment task designing or the teachers’ shared belief of assessment culture in the given context. This is evident from the dominance of SRQs in most of the tasks. It cannot be a mere coincidence that instructors with Ph.D. degrees as well MA qualifications design almost similar tasks. Previous research has also shown that teachers’ assessment task designing practices are often dictated by different stakeholders such as students, parents and community (Cheng, 1997). Therefore, further investigation may reveal the reasons for this undesirable assessment approach.
Teachers’ perception plays a critical role in their approach to teaching. Cheng (2002) has remarked that teachers’ perceptions concerning teaching emerge from various areas such as their personal learning and teaching experiences along with the kind of education system they have been students of. Their beliefs, values and objectives with regard to the syllabus and teaching methods are influenced by their perceptions experiences. Such perceptions also affect their concept of the curriculum they teach and their specific roles within it. Finally, perceptions influence their decision making and actions. The most significant factor forming teachers’ approach to teaching and learning is their familiarity with syllabus, skills and content assessed in a test (Alderson and Wall, 1993). The greater the knowhow, the more is the influence on pedagogic practices. Therefore, desirable alignment between teachers’ perceptions and the intended learning outcomes is indispensable and if not assessment literate already, they need to have adequate assessment literacy.
Conclusion and Recommendations
This research was based on the analysis of only nine courses (total number of courses was 36) of an English-major program. Its findings, therefore, may not be generalizable unless the assessment tasks of the whole program are evaluated. However, in the context of assessment tasks mapping with CLOs, this study has cast serious doubts on the validity of assessment tasks that can guarantee quality assurance required by NQF standards. The assessment tasks evaluated were completely invalid. They did not measure what they were supposed to measure. Evidence from previous research indicates that assessment tasks that are authentic and actually measure target CLOs have greater prospects of inculcating higher-order learning whereas assessment instruments with SRQs result in surface-level learning. Therefore, it can be safely stated that the English major summative examination is very far from promoting higher-order learning. Further research into the alignment between CLOs and assessment tasks of English major programs from another Saudi university will show the extent this problem contributes to the low quality of students’ learning nationwide. Experimental studies, in particular, may show how assessment tasks having greater congruence with CLOs can ascertain quality assurance required by NCAA/NQF. Future research may seek teachers (assessment task designers) input to determine the factors contributing to their current assessment practices and literacy.
References
- Alderson, J.C.,and Wall, D. (1993). Does washback exist? Applied Linguistics, 14(2), 115-129.
- Archbald, D.A. and Newmann, F.M. (1988). Beyond standardized testing; Assessing authentic academic achievement in secondary school. Madison. WI: National Center on Effective Secondary Schools. Retrieved on 11/04/2016 from the ERIC database
- Benedetti, K.D. (2006). Language testing: Some problems and solutions. Mextesol, 30(1)
- Boud, D. Cohen, R. & Sampson, J. eds. (2001). Peer learning in higher education. London: Routledge
- Burrows, C. (2004).Washback in classroom-based Assessment: A study of the washback effect in thenAustralian adult migrant English program. In L. Cheng, Y. Watanabe, and A. Curtis, (Eds.), Washback in language testing; Research context and methods (pp.113-128), London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Chen, L. (2002). Washback of a public exam on English teaching. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED472167).
- Cheng, L. (2004). The washback effect of a public examination change on teachers' perception toward their classroom teaching. In L. Cheng, Y. Watanabe, and A. Curtis, (Eds.), Washback in language testing; Research context and methods (pp. 147- 170), London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Cheng, L. (1997). How does washback influence teaching? Implications for Hong Kong. Language and Education, 11, 38-54.
- Cheng, L. and Curtis, A. (2004).Washback or Backwash: A Review of the Impact of Testing on Teaching and Learning. In L. Cheng, Y. Watanabe, and A. Curtis, (Eds.), Washback in language testing; Research context and methods (pp. 3-17). London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Coombe, C. and Evans, J. (2005). Writing assessment scales: Making the right choice. In D. Lloyd, P. Davidson, and C. Coombe (Eds.), Fundamentals of Language Assessment: A Practical Guide for Teachers (pp. 99-104). Dubai: TESOL Arabia Publications.
- Denscombe, M. (2007). The Good Research Guide: For small-scale social research project (3ird Ed.). Buckingham: Open University Press.
- El-Ebyary, K. (2009). Deconstructing the complexity of washback relation to formative assessment in Egypt. Cambridge ESOL: Research Notes, 35, 2-5.
- Ferman, I. (2004). The washback of an EFL national oral matriculation test to teaching and learning. In L. Cheng Y. Watanabe, and A. Curtis, (Eds.), Washback in language Testing; Research context and methods (pp. 191-210), London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Frankland, S. ed. (2007). Enhancing teaching and learning through assessment. Dordrecht: Springer.
- Gijbels, D. and Dochy, F. (2006). Students' assessment preferences and approaches to learning: Can formative assessment make a difference? Educational Studies, 32(4), 399-409.
- Gijbles, D., Segers, M. and Struyf, E. (2008). Constructivist learning environments and the (im)possibility to change students' perceptions of assessment demands and approaches to learning. Instr. Sci., 36, 431-443.
- Green, A. (2007a). IELTS washback in context: Preparation for academic writing in higher education. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Green, A. (2007b). Washback to learning outcomes: A comparative study of IELTS preparation and university pre-sessional language courses. Assessment in education. 14(1), 75-97.
- Green, A. (2006). Watching for washback: Observing the influence of the International English Language Testing System academic writing test in the classroom. Language Assessment Quarterly, 3(4), 333-367
- Manjarrés, N.B. (2005).Washback of the foreign language test of the state examinations in Colombia: A case study. Arizona Working Papers in SLAT, 12, 1-19.
- Messick, S. (1996). Validity and washback in language testing. Language Testing, 13(3), 241-256
- Messick, S. (1993). Foundations of validity: meaning and consequences in psychological assessment. ETS Research Report , 2, i18. DOI: 10.1002/j.2333- 8504.1993.tb01562.x
- Muñoz, A.P. and ÃÂlvarez, M.E. (2010). Washback of an oral assessment system in the EFL classroom. Language Testing, 27(1), 33-49.
- National Commission for Academic Accreditation and Assessment (2017). Handbook for quality assurance and accreditation in Saudi Arabia. Retrieved from
- Paul, P.V. (Ed.) (2008). Language and deafness (4th Ed.). London: Jones and Barlett
- Saif, S. (2006). Aiming for positive washback: A case study of international teaching assistants. Language Testing, 23(1), 1-34.
- Saville, N. and Hawkey, R. (2004). The IELTS impact study: Investigating washback on teaching materials. In L. Cheng, Y. Watanabe, and A. Curtis, (Eds.), Washback in language Testing: Research context and methods (pp.73-96). London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Scouller, K. (1998).The influence of assessment method on students' learning approaches:Multiple choice question examination versus assignment essay. Higher Education, 35,453-472.
- Stecher, B., Chun, T. and Barron, S. (2004). The effects of assessment- driven reform on the teaching of writing in Washington State. In L. Cheng, Y. Watanabe, and A. Curtis, (Eds.), Washback in language Testing; Research context and methods (pp.53-71). London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Cite this article
-
APA : Umer, M., & Soomro, A. F. (2019). Outcome-Based Assessment and Saudi National Qualifications Framework: An Evaluation of English-Major’s Summative Examinations. Global Language Review, IV(I), 18-27. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2019(IV-I).03
-
CHICAGO : Umer, Muhammad, and Abdul Fattah Soomro. 2019. "Outcome-Based Assessment and Saudi National Qualifications Framework: An Evaluation of English-Major’s Summative Examinations." Global Language Review, IV (I): 18-27 doi: 10.31703/glr.2019(IV-I).03
-
HARVARD : UMER, M. & SOOMRO, A. F. 2019. Outcome-Based Assessment and Saudi National Qualifications Framework: An Evaluation of English-Major’s Summative Examinations. Global Language Review, IV, 18-27.
-
MHRA : Umer, Muhammad, and Abdul Fattah Soomro. 2019. "Outcome-Based Assessment and Saudi National Qualifications Framework: An Evaluation of English-Major’s Summative Examinations." Global Language Review, IV: 18-27
-
MLA : Umer, Muhammad, and Abdul Fattah Soomro. "Outcome-Based Assessment and Saudi National Qualifications Framework: An Evaluation of English-Major’s Summative Examinations." Global Language Review, IV.I (2019): 18-27 Print.
-
OXFORD : Umer, Muhammad and Soomro, Abdul Fattah (2019), "Outcome-Based Assessment and Saudi National Qualifications Framework: An Evaluation of English-Major’s Summative Examinations", Global Language Review, IV (I), 18-27
-
TURABIAN : Umer, Muhammad, and Abdul Fattah Soomro. "Outcome-Based Assessment and Saudi National Qualifications Framework: An Evaluation of English-Major’s Summative Examinations." Global Language Review IV, no. I (2019): 18-27. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2019(IV-I).03