Abstract
This study investigates the phenomenon of verb agreement (subject-verb agreement) in Lasi and English. This study focuses only on transitive and intransitive verbs of simple tenses to analyze the subject-verb agreement in Lasi. The data have been collected through unstructured interviews with the Lasi natives. The X-bar theory of Haegeman (1994) has been applied as a theoretical framework. Descriptive and exploratory research designs (Creswell, 2014) are used in the study. The results of this study show that transitive verbs in Lasi agree with subjects in number, gender, and person in the present and future tenses, but not in the past. However, intransitive verbs do agree with their subjects in the past tense. English verbs show agreement with their subjects in the present simple tense, but their past and future tense inflections remain the same. The results show that Lasi allows omission of subjects in the surface structure; however, they are recoverable in deep structure.
Key Words
Lasi, English, Subject-Verb Agreement, Inflections, X' Theory
Introduction
The
subject-verb agreement is a linguistic feature
which means changes happen in verbs according to the subject. The
subject-verb agreement refers to the study of different inflections in relation
to syntax. The main purpose of this study is to analyze the subject-verb
agreement in Lasi.
Bukhari (1947) argues that the state of Lasbela lies in the west of
Karachi. The main language of the people of Lasbela is Lasi which is one of the
dialects of Sindhi. Zahid (2016)
explains that Sindhi is a spoken language in the sub-continent. The number of
speakers is almost 78 million; 25 million speakers speak Sindhi in India and 25
million speakers speak Sindhi in other different countries. Jumani and Lashari (2011)
explained that Sindhi is a family member of Arabic, Persian, Sanskrit, Urdu,
and Hindi. It's from right to left in written taking Perso-Arabic script. In
contrast, western languages are written from left to write. The Sindhi/Lasi
language is written in four scripts: Gurmukhi, Arabic, Roman scripts, and
Devanagari (Ali, Z., 2016).
Cole (2001)
suggests that morphologically, Sindhi is a rich inflectional and derivational
language. Suffixes are added, subtracted, and replaced. Sindhi words always end
in a vowel. According to Cole (2001), the
basic word order of Sindhi is SOV, but the alternate word order is also
possible in the spoken language without changing the meaning, so Sindhi is
called free word order. For example:
|
Chhokry kitab parhyo. |
SOV |
|
Kitab Chhokry parhy. |
OSV |
|
Parhyo kitab chokry. |
VOS |
|
Chhokry parhyo kitab. |
SVO |
|
Kitab parhyo chhokry. |
OVS |
|
Parhyo chhokry kitab. |
VSO |
|
The boy reads the book. |
|
The
Sindhi language is an old language of the world. Regarding the origin of the
Sindhi language, different scholars have different opinions. Trump (2011)
and Stack (2011)
explain that the Sindhi language appears in the eleventh century. According to
him, there are a lot of Sindhi words that show that Sindhi is derived from
Sanskrit. According to Allana (2009),
Sanskrit scholars' views also are that Sindhi has been taken from Sanskrit
because there are a lot of similarities in phonetics and morphology are found
between these two languages. Baloch (1962) views
that Sindhi has been taken from Indo-Aryan Indus Valley languages. Sirajul Haq
Memon (1964), cited in Allana (2009), argues
that Sindhi has not been derived from Sanskrit, but on the other hand, Sanskrit
was taken from Sindhi because the people of old Sindh had migrated to
Mesopotamia and Babylonia. They had taken their language with them, and it
spread there. Grierson (1919)
expresses his views that Sindhi belongs to the northwestern group of the
Indo-Aryan dialects.
The Sindhi Dialects
According
to Pirzado (2009),
there are six dialects of the Sindhi language: Siroli, Vicholi, Lari, Kohistani, Thareli/ Kuchhi and Lasi. The dialect Siroli is spoken northern area and upper part of Sindh. The word "Siro" means in Sindhi' Head'
or upper. The dialect Vicholi is
spoken in the central part of Sindh. The word "Vicholi" has been taken from the Sindhi word "vich-u" which means center or
middle. This dialect is said to be a standard dialect. It is used in education,
media, and literature. The Lari dialect
is spoken in lower Sindh, including Hyderabad, Thatta, Badin and Indus Delta.
The word Lar means sloping; it is
applied to the lower Sindh. Kachi and
Thareli are both mixed dialects.
According to Baloch (2008) and Pitafi (2009),
Sindhi is spoken in 12 various dialects used in Sindh and a few districts of
Balochistan. Among them, the Vicholi dialect
is considered the standard dialect of Sindhi.
Lasi
Amin & Ali (2021)
argue that the term Lasi is a geographical name that is used for all tribes
that are locally living in Lasbela. There are five major tribes; Roonjha,
Jamot, Burah, Shaikh and Angaria, including their brotheries which speak Lasi.
According to the censuses report of 1998, Lasbela is divided into 9 Tehsils:
Bela, Lakhara, Lyari, Uthal, Durreji, Gadani, Sonmiyani, Hub and Kanraj. Allana (2010)
argues that many tribes have migrated from Sindh to Las in ancient times; they
spread their culture and language here. According to him, in the times of Arab,
Sumra and Summan had migrated to Las and resident Las. According to Grierson (1919),
Lasi is the form of Sindhi language which is spoken in Las; it semantically and
morphologically differs from Sindhi.
Problem Statement
Greirson
(1919) and Baloch (2008) have done very little work on the
phonology and morphology of the Lasi dialect. According to them, Lasi differs
phonologically and morphologically from standard Sindhi. In Lasi, like Lari dialect, words are shortened such as 'baar' (outside) for 'baahar'. Thus, in Lasi aspirated consonant becomes unaspirated
like 'budo' for 'budho' (heard), and auxiliary 'tho’
becomes ‘to’ in lasi. The
interrogative pronoun ‘chha=what’ is
produced ‘chho’ in Lasi, and ‘chho’ means ‘why’ in Sindhi. However,
this dialect has been morphologically and syntactically ignored all this while;
there has not been any work so far (Veesar, & Mustafa,
2021).
This
research study attempts to analyze and explore such differences and their
possible effect on sentence structure (subject-verb agreement). This study examines the nature of the subject-verb
agreement in Lasi compared with English. Lashari and Soomro (2013)
argue that verbs in English show agreement in the present tense with their
subjects in number and while Sindhi syntactically is exhaustive, its verb
agrees with the subject in number, gender, person, tense, aspect, and mood in
all tenses. The following examples show these differences.
|
Sindhi |
Lasi |
English |
|
Maan likhaan tho. |
Aaon likhan to. |
I write. |
|
Hoowa likhy thi. |
Owa likhy ti. |
She writes. |
|
Uhy likhan tha. |
Ho likhan ta. |
They write. |
|
Assan likhaon tha. |
Ason likhon ta. |
We write. |
The above examples show that the verb is differently
inflected for the person, number, and gender in Sindhi and Lasi. The inflection
‘tho’ changes into ‘to’ in Lasi, according to the gender,
number, and person of the subject. However, the English verb is inflected with
the morpheme ‘s’ or
‘es’ for third-person singular. For other subjects, plain form is used. The
infection in the verb does not show the gender of its subject in English.
Objectives of Study
The
study attempts to analyze the position of
subject-verb agreement in different word ordering of Lasi sentences and to
explore the verbs which do not agree with the subjects.
Literature Review
Morphology
Rahman (2009) argues that morphology explains word formation and rules in the language. Morphology defines how morphemes are attached to words. Morphology also represents the variations within the words. According to Bauer (1983), Morphology is an element of linguistics that provides information about the internal structure of words. The basic unit of morphology is a morpheme. A morpheme is divided into two types: free morpheme and bound morpheme. A free morpheme can occur in isolation, while a bound morpheme cannot occur in isolation. Zahid (2016) and Surahio & Jumani (2016) divide free morphemes into lexical and functional morphemes and bound morphemes into derivational and inflectional morphemes.
Das, P., & Barbora, M. (2020) explain that inflectional morphemes are those bound affixes through which new words with different forms but the same meaning are made from an existing stem. They are used to make plural or past tense. For example, plurals: buses–bus and past tense: die–died. Derivational morphemes create new words. It often belongs to a different syntactic category. They are used to make a noun from an adjective or an adjective from a verb. Example: an adjective to noun: happy– happiness. Adjective to a verb: commercial–commercialize. Varshney (1995) classifies morphemes into roots and affixes: root morphemes are those which are left after removing all affixes; they may be free or bound. Affixes are those morphemes that cannot stand alone. They are bound. For example, the English word 'unfaithful' has three morphemes: 'un,' 'faith' and ful. ‘Faith’ is a root while ‘un’ and ful are affixes. He further divided affixes into prefix, suffix, and infix. Prefix those bound morphemes that are affixed before the root, and suffixes are affixed at the end of the root. Infixes are affixed in the word. English has a rich derivational system of morphology; it has many derivational suffixes and prefixes. These suffixes and prefixes are added to a root and form a stem. English has meager inflection suffixes which are added to the stem and form a finishing word (Dixon, 2014).
Morphology of Sindhi
Cole (2001) argues that morphologically Sindhi is a rich inflectional and derivational language. Suffixes are added, subtracted, and replaced. Sindhi words always end in a vowel. Rahman (2009) suggests that Sindhi has two types of words: the first one is primary words and the second one is secondary words. Primary words are those that are not breakable. These words are said to be morphemes. For example, ‘rasto’ (path, way) and ‘hari’ (farmer). Secondary words are divided into complex words and compound words. Complex words are those which are made by combining prefixes or suffixes with root words for example root word ‘jjan’ (knowledge) combines with prefix (??) ‘ann’ (a prefix which negates the meaning) then it becomes ‘unjjan’ (layman) and when suffix ‘o’ attached with root word ‘jjan’ it becomes ‘jjano’ (scholar). Compound words are made by combining two same or different simple words without bound affixes. In Sindhi, derivational morphology is the result of the combination of a root word with a grammatical morpheme which forms a word with a different class. For instance, a noun is formed from a verb and an adjective is made from a noun. Sindhi derivational morphology is changed by affixes. The inflectional morphology in Sindhi is the result of the combination of a root with a morpheme which forms a word with the same class (Ali, Z., Bagddu, R.S., & Maimota, M.S., 2014; Ali, Roonjho & Brohi, 2021; Ali, Khan & Gulkhanda, 2021; Ali & Muhammad, 2021). According to Devi (2012), morphologically, Sindhi is a very rich language in terms of inflection morphemes and derivations morphemes as prefixes and suffixes. According to him, there are two categories of words in Sindhi: primary and secondary words. The primary lexemes are breakable. On the other hand, the secondary lexemes are categorized into compound words (the group of two or more than two primary words known as compound words) and complex words (the adding of affixes). Sindhi language Morphologically traits verbs trunks (stems), objective (impersonal) and reflexive (passive), and post-positions, nouns and verbs used along with suffixes pronouns.
Baig (2006) and Rahman (2009) argue that Sindhi nouns are either singular or plural. Baig gives the following principles for noun number inflection in terms of their gender and ending vowels:
1. The ending ?? inflection with singular feminine noun changes into ???? for a plural feminine noun.
2. The ending ?? inflection with singular feminine noun changes into ?? for a plural feminine noun.
3. The ending ?? inflection with a singular feminine noun changes into for plural noun.
4. The ending ?? inflection with singular feminine noun changes into ???? inflection for a plural noun.
5. The ending ?? inflection with singular feminine noun changes into ???? inflection for a plural noun.
6. The ending ?? inflection with masculine nouns changes into ?? inflection for a plural noun.
Subject-Verb Agreement in English
Haegeman (1994)
argues that in English, the verb has two forms in the present tense and only
one form in the past tense. Lashari and Soomro’s study (2013)
also align with Haegeman. For example:
|
Singular |
Plural |
|
I eat. |
Ali and Sam eat. |
|
You eat. |
You eat. |
|
He/she/it eats. |
We eat. |
However,
verbs in past and future do not change the form for 1st, 2nd,
and 3rd person subjects. For example:
|
I walk. |
We walked. |
|
You walked. |
You walked. |
|
He or She walked. |
They walked. |
|
I will walk. |
We will walk. |
|
You will walk. |
You will walk. |
|
He/ she will walk. |
They will walk. |
The Verb Agreement in Sindhi
Baig (2006) uses the word ‘Nisbatoon’ or ‘Paryoog’ for
the English word ‘agreement.' He divided verb agreement into three types:
subjective construction, objective construction, and neuter construction.
Subjective construction: the word ‘Kartar’ or ‘Karta’ means ‘Faail’ (subject)
and the ‘Kartary’ means ‘Faailey’ (subjective). In this construction, the verb
shows agreement with the subject and in its number, gender, and person.
Objective construction: the word ‘karam’ means ‘mafaool’ (object) and Karmani
means ‘mafaooly’ (objective). In such constructions, the verbs show agreement
with the object. Neuter construction: in this type of agreement, the verb does
not show agreement with the subject or object but remains neuter.
Research Methodology
This
section refers to the research design, data selection, data collection, data
description, data transcription, data analysis and X bar theory by Haegeman (1994). X’ Theory by Haegeman (1994) is used to draw a tree diagram to represent Lasi
sentence focusing on verb phrase, especially on INFL and word order of sentence
to see subject-verb agreement.
Research Design
This
research work is qualitative in nature, using exploratory and descriptive
research designs (Creswell, 2014;
Kumar, 2011).
These designs are used to explore and understand
the nature and agreement of Lasi verbs. The study describes the Lasi verbs at
first and then explores their forms and functions from the perspective of
morphosyntax.
Data Collection
In
a qualitative method, an interview
is a commonly used technique for collecting the data. An interview is a
face-to-face verbal conversation between interviewer and interviewee; it may be
through telephone or recording (Kumar, 2011). An interview is the most direct and straightforward
method to collect detailed data regarding a particular problem.
Interviews may be structured or unstructured; structured interviews are those
through which the researchers ask preplanned questions, whereas unstructured
are those through which the researchers do not ask preplanned questions (Kumar, 2011).
The unstructured interview technique has been used to collect the data in this
study. The data have been collected from the Lasi natives in the verbal
form which are later transcribed and codified into non-verbal form.
Theoretical/Analytical Framework
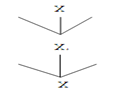
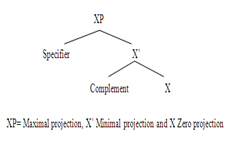
The data have been analyzed through X’ Theory of phrase structure by Haegeman (1994). This theory was used to draw a tree diagram to represent Lasi sentences focusing on verb phrases, especially on INFL. The theory tells about the common in the phrase structure. According to the theory, one head is headed to all phrases. The head of the projection is a zero projection (XO). Head dominates words because heads have terminal nodes. X to for X'-projections are combined by Complements and X to for X'-projections are combined by adjunts. The specifier combines with the topmost X' to form the maximal projection XP.
In the above tree diagram, X stand for N, V, A OR P. The general format for phrase structure is summarized in the following PS rules:
Lasi is head-last and specifier-first language. Therefore, its basic phrase structure rule is:
Data Analysis and Discussion of Lasi Sentences
Sentences
This section deals with the analysis of different
verbal inflections in Lasi to see the subject-verb agreement in tense, person,
number, and gender. Subject-verb agreement is a
linguistic feature that shows changes through subject variation.
The analysis section discusses the inflections in transitive and intransitive
verbs; these verbs are in indicative moods with simple tenses. It presents the
structure of sentences (word order) to see whether the verb shows agreement
with the subject in different word orders. The study adopts the X’ theory
of Haegeman (1994)
to make a tree diagram to see the subject-verb agreement and the sequential
order of words in sentences.
Subject-Transitive Verb Agreement
The
subject is the doer of the action in a typical clause (Haegeman, 1994).
Transitive verbs are those whose meaning is incomplete without a direct object (Baig, 2006).
The following examples analyze the inflections of intransitive verbs in
present, past and future simple tenses to see the subject-verb agreement in
Lasi.
Present Simple
Example 1: Gaon kheer dayti. (Cow gives the milk.)
|
Gaon |
kheer |
dayti |
|
Cow |
milk |
gives |
|
N (SUB)-sg-f |
N (OBJ) |
V (sg-f) |
Figure 1
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram shows an agreement configuration between the subject and the
head AGR (agreement). They agree with features such as number, gender, person,
tense, and aspect. The above sentence presents a simple present tense. The
sentence structure (word order) is SOV. The subject ‘gaon’ (cow) is singular in number and feminine in gender, and it
has a nominative case because noun is not inflected in nominative case with any
case marker; it remains in its original form (Rahman, 2009).
The
verb ‘dayti’ (gives) is a transitive
verb with two arguments, 'gaon=cow’ and ‘kheer=milk.' According
to Allana (2010)
and Alshammiry,
K. (2016), a transitive verb requires a subject and
needs an object because they make complete sense. The verb ‘dayti’ (gives) is derived from ‘deyan’ (to give). This form is infinitive and infinitive has been
taken from the imperative form 'dy’ (give).
The verb is inflected with the inflection ‘ti’
(agreement), which is phonologically produced ‘thi’ in Sindhi Baloch (2008), to
show that the subject is singular in number and feminine in gender. It also
indicates that the action has occurred in the present time. English uses ‘s’ or ‘es’ with verbs to show the
number and person of arguments (3rd person singular subjects) and a
plain verb form with 1st, 2nd and 3rd person
plural subjects. However, in Lasi, the verb is inflected according to gender,
number and person of the subjects. For example, in the replacement of a
singular feminine subject with the plural feminine subject, the inflection with
the verb will be ‘tiyoon’
(agreement). With singular masculine subject, the inflection will be ‘to’ with the plural masculine subject,
the inflection will be ‘taa.'
Example
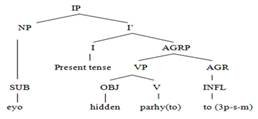
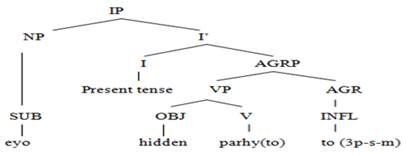
2: Eyo parhaayto. (He teaches.)
|
Eyo |
parhaay |
to |
|
He |
teaches |
agreement
marker |
|
SUB
(3p-sg-m) |
V
(3p-sg-m) |
|
Figure 2
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram shows that the AGR and [Spec, AGRP] agree in gender, number,
person, tense and aspect. The construction of this statement explains that it
is spoken in the present tense with SOV word order. The subject ‘eyo’ (he) is a third person pronoun
having a masculine gender singular number with a subjective/nominative case.
The
verb ‘parhaayto’ (teaches) is a
transitive having a vivid subject and a hidden object in the surface structure
of the sentence. The speaker did not use the object, but the context shows that
the verb has an object argument. The verb ‘parhyto’
(teaches) is taken from the infinitive form ‘parhain’
(to teach) which is taken from the root form ‘parhaai’ (teach) which is further derived from the imperative ‘parh’
(read/study). This verb contains two inflections: the first inflection, ‘aay’ (agreement) in the verb ‘parhaay’ indicates that subject is the
third-person pronoun. This inflection will change according to the persons of
pronoun subjects. With the first-person pronoun subject, the inflection with
the verb will be ‘yaan’ (agreement).
Thus, with the second-person pronoun subject, the inflection with the verb will
be ‘een’ (agreement). The last
inflection ‘to’ (agreement) in the
verb ‘parhaayto’ (teaches) shows the
present simple tense; this morpheme also shows that subject is singular in
number. With the changing of a singular subject into a plural subject, the
inflection ‘to’ (agreement) changes
in ‘taa’ inflection. This inflection
also shows that subject is masculine in gender. Unlike English, where the verb
does not agree in gender, but in Lasi verb agrees with the subject in gender as
the changing of a masculine subject with the feminine subject, the inflection ‘to’ (agreement) with the verb ‘parhaAyto’ (teach) will change in ‘ti’ (agreement).
Past Simple Tense
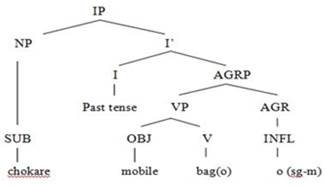
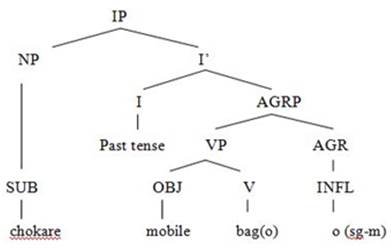
Example 3: Chokare mobile bago. (Boy broke the
mobile)
|
Chokare |
mobile |
bago |
|
Boy (s-m-obl) |
mobile (Nom) |
broke |
|
SUB (sg-m) obl |
OBJ (sg-m) |
V (sg-m) |
Figure 3
Tree Diagram
The above sentence presented in example 3 is
in the simple past tense. The structure of this sentence is SOV. The subject ‘chokare’ (boy) is inflected with the
case marker 'e,' so it is in oblique
case because in the accusative, dative, postpositional and genitive cases,
nouns are inflected (Ali, Z., 2016). This inflected form is called the oblique
case (Rahman, 2009).
According to Baig
(2006), ‘chokare’
(boy) is in the oblique case and ‘chokaro’
(boy) is the nominative case in Sindhi/Lasi. The verb ‘bago’ (broke) is transitive in Lasi because it has an object mobile. The verb ‘bago’ (broke) is derived from the infinitive verb ‘bajan’ (to break) and the infinitive ‘bajan’ is derived from the imperative
form ‘banj’ (break). The inflection ‘o’ (agreement) with verb does not show
the gender and number of subjects. With all subjects, either singular or plural
and masculine or feminine same inflection ‘o’
(agreement) is used with the verb ‘bago’
(broke), as the verb is in the simple past tense. Verbs in simple past tense do
not agree with subjects but with objects in Lasi/Sindhi (Ali, Z., 2016). The
inflection ‘o’ (agreement) shows the
gender and number of objects mobile because
the transitive verb in past tense shows the agreement with the object.
According to Ranjan
(2016), the subject seems “ne” marker which is an
ergative case marker. In the case of the perfective aspect, the verb is
transitive, and the verb agrees with the nominative object DP. If the object is
plural, the inflection ‘o’ (agreement)
changes
into ‘aa’ (agreement) and with the
feminine object, the inflection ‘o’
changes into ‘ee’ (agreement).
Example 4: En
college ma dakhlo wato. (They took the admission to college)
|
En |
college |
ma |
dakhlo |
Wato. |
|
They |
college |
in |
admission |
took (past) |
|
SUB (obl- pl-m) |
N |
P |
OBJ (nom-sg-m) |
V (sg-m) |
Figure 4
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram shows an agreement configuration between the object and the
head AGR. They share features such as number, gender, and person. The above
sentence presented in example 4 is in the simple past tense. The subject ‘en’ (they) is the third person plural
masculine pronoun subject and has an oblique form because in Sindhi/Lasi ‘uhy’ (they) is nominative in the case
and ‘en’ (they) is in an oblique case
(Baig, 2006).
The object ‘dakhlo’ (admission) is
singular in number and masculine in gender, having an accusative case. The verb
‘wato’ took has come from the
infinitive form 'wathan’ (to take),
and the infinitive ‘wathan’ has come
from the imperative form ‘wath’
take.
The inflection ‘o’ (agreement) with
the verb ‘wato’ (took) shows that the
action has taken place in the past time. It also shows the number and gender of
the nominative object 'dakhlo’
(admission). This inflection ‘o’ (agreement)
changes to the gender and number of objects accordingly. For example, with the
plural object, the inflection ‘o’ (agreement)
with verb changes into ‘aa’
(agreement) inflection. Thus, with a feminine object, the inflection ‘o’ (agreement) with verb changes into ‘ee’ (agreement).
Future Simple
Tense
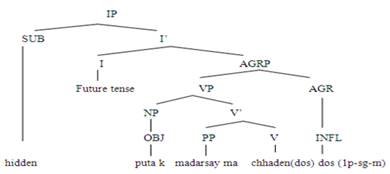
Example 5: Putak madarsym chadindos. (I) will
send/leave son in school)
|
(Null sub) |
Puta |
K |
madarsy |
m |
chadindos |
|
|
son |
to |
School |
in |
will send/leave |
|
SUB (null) |
OBJ |
P |
N |
P |
V (1p-s-m) |
Figure 5
Tree Diagram
The above tree diagram shows an agreement
configuration between the subject and the head AGR. They share features such as
number, gender, and person. The above sentence of Lasi Language subject does
not exist in the surface structure. The verb ‘chadeendos’ (will send/leave) verb is a transitive form with a
hidden object and subject argument ‘puta’
(son). The verb ‘chadeendos’ has
been taken from the infinitive form ‘chadan’
(to send/leave) and the infinitive has been taken root word ‘chad’ (leave). The inflection ‘dos’ (agreement) in the verb ‘chadeendos’ (will leave) is used to
indicate that the subject is the first person pronoun. With the replacement of the
second
person pronoun with the first-person pronoun subjects, the inflection will be ‘dohen’ (agreement). With the third
person pronoun subject, it will be ‘do’
(agreement). The inflection ‘dos’ (agreement)
shows that subject is singular in number. In the case of the plural subject,
the inflection ‘dos’ (agreement) will
change into ‘dasen’ (agreement). This
inflection also shows that subject is masculine in gender because the suffix ‘dos’ (agreement) is used for masculine
gender agreement and ‘dias’ (agreement)
for feminine gender agreement in the future tense in Lasi/Sindhi (Zahid, 2016).
Example 6: Diya Moosani ma parhandi. (Daughter will
study in Moosani.)
|
Diya |
Moosani |
ma |
parhandi |
|
girl |
Moosani |
in |
will study |
|
SUB (s-f) |
N |
P |
V (s-f) |
Figure 6
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram shows the sentence in future simple tense with an SV order.
The subject ‘diya’ (girl/daughter) is
singular in number and feminine in gender and has a nominative case. The verb ‘parhandi’ (will study) is a transitive
verb with a clear subject and a hidden object. The verb ‘parhandi’ (will study) is taken from ‘parhan’ (study) which is the infinitive form, and this infinitive
took from the imperative form ‘parh’ (study/read).
The inflection ‘di’ (agreement) in the verb ‘parhandi’ (will study) indicates the feminine in gender and
singular in the number of subjects and it shows future simple tense too. In the
case of the plural subject, the inflection
‘di’ (agreement) will change into ‘diyon’
(agreement) and in the case of the masculine subject, the verb ‘parhandi’ (will study) will terminate
into ‘to’ (agreement) inflection.
Subject-Intransitive
Verb Agreement
An
intransitive verb is that which does not require a direct object (Ali, 2016).
Following examples, analyze the inflections and conjugations in intransitive
verbs to see the nature of the subject-verb agreement in Lasi.
Present Simple
Example
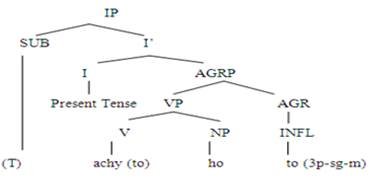
7: Achyto ho. (He comes.)
|
Achay |
to |
ho |
|
comes |
agreement marker |
he |
|
V (sg-m) |
|
3rd PRO (SUB) sg-m |
Figure 7
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram presents example 7 in the present simple tense. The
structure of the above sentence is VS. The subject ‘ho’ (he) is singular in number, masculine in gender and has a
nominative case. The verb ‘achyto’ (comes)
is intransitive because it does not require an object argument. It has taken
its root from the infinitive verb ‘achan’
(to come), and infinitive has taken its root from the imperative form ‘ach’ (come). The verb ‘achyto’ (comes) contains two
inflections: the first inflection in the verb ‘y’ (agreement) ‘achyto’ (comes)
identifies the third person of the pronoun subject. This inflection will change
according to the persons of pronoun subjects. For example, in the case of
second-person pronoun subject, the inflection ‘y’ (agreement) will change into ‘een’ (agreement), and in the case of first-person pronoun subject,
this inflection will change into ‘an’
(agreement).
The
second inflection, ‘to’ (agreement) with the verb ‘achyto’
(comes), is used to indicate the present simple tense; it also identifies
the singular number of subject ‘ho’
(he). This inflection also changes according to the number of subjects. For
example in the case of the plural subject, this inflection ‘to’ (agreement) changes into
‘taa’ (agreement. The inflection ‘to’ (agreement) with the verb ‘achyto’ (comes) also shows that subject
is masculine in gender. This inflection ‘to’
(agreement) changes according to the gender of subjects in Lasi. For
example, in the case of the feminine subject, the inflection ‘to’ (agreement) changes into ‘ti’ (agreement).
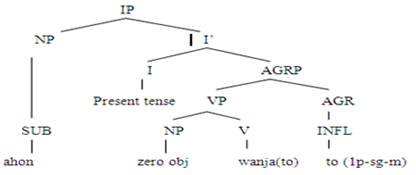
Example 8: Ahon wanjato. (I go)
|
ahon |
wanjan |
to |
|
i |
go |
agreement marker |
|
SUB (1p sg-m) |
V (sg-m) |
|
Figure 8
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram shows that the AGR and [Spec, AGRP] agree in gender, number,
and person. The above sentence presented in example 8 is in present simple. The
structure of this sentence is SV. The subject ‘ahon’ (I) is the first person pronoun having masculine in gender
and singular in number, and this sentence is nominative in case. The verb ‘wanjanto’ (go) is intransitive because
it does not require an object argument. So, it gives complete meaning without
an object. The verb ‘wanjanto’ (go)
is taken from the infinitive form ‘wanjan’
(to go) and the infinitive is taken from the imperative ‘wanj’ (go).
The
verb ‘wanjanto’ (go) contains two agreement markers or inflections. The first
inflection ‘an’ (agreement) in verb ‘wanjanto’ (go) indicates that the subject is the first-person pronoun. This
inflection changes according to the person of pronoun subjects. With the
replacement of the first-person pronoun subject with the second-person pronoun
subject, the inflection will be ‘een’ (agreement). Thus, for the third-person pronoun
subject, it will be ‘y’ (agreement).
While the last inflection with the verb ‘to’ (agreement) refers to the simple
past tense, it also shows a singular number of subjects. This inflection
changes according to the subject's number. If the subject is plural, the
inflection ‘to’ (agreement) changes into ‘taa.'
Apart from that, this inflection shows the masculine gender of the subject.
In the case of the feminine subjects, this inflection changes in inflection ‘tiyon.'
Past Simple
Tense
Example 9 Eyay Bajjiwya. (They ran away.)
|
Eyay |
bajjiwya |
|
They |
ran away (past) |
|
SUB (3p-p-m) |
V (3p-p-m) |
Figure 9
Tree Diagram
The above tree diagram shows that the AGR and
[Spec, AGRP] agree on gender, number and person. The structure of this sentence
is SV. The subject ‘Eyay’ (they) is a
third-person pronoun having masculine in gender and plural in number and has
come without any case marker, so it is nominative in case.
The verb ‘bajjiwya’
(ran away) took from the verb which is infinitive ‘bajji wajan’ (to run away) and the infinitive verb ‘bajjiwanan’ (to run away) was taken
from the root verb 'bajj’ (run). It
is an intransitive verb. The inflection ‘wya’
(agreement) with the verb ‘bajjiwya’
(ran away) shows that subject is the third person pronoun subject. This
inflection changes according to the persons of pronoun subjects. With the
second person pronoun subject, the inflection with verb will be ‘yahoon’ (agreement); and with the
first-person pronoun subject, the inflection with verb will be ‘yasen’. The inflection ‘ya’ (agreement) in verb ‘bajjiwya’ (ran away) shows that subject
is plural in number, and it also shows the simple past tense. By changing the
plural subject into a singular subject, the inflection ‘ya’ in the verb ‘bajjiya’ (ran
away) will change into ‘yo’ inflection
and with the changing of the masculine subject into the feminine subject, the
inflection ‘ya’ will also change into
‘yon’ inflection.
Example 10: Mein wasyo. (It rained/ It is rained)
|
Mein |
wasyo |
|
rain |
fell (past) |
|
SUB (sg-m) |
V (sg-m) |
Figure 10
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram shows that the AGR and [Spec, AGRP] agree in person, number
and gender. The above sentence presented in example 10 is past simple. The
structure of this sentence is SV. The subject ‘Mien’ (rain) is singular in number and masculine in gender, having
a nominative case. The verb ‘wasyo’
(rained) took from the verb ‘wasan’ (to
rain) and it is infinite. The infinitive verb ‘wasan’ (to rain) is derived from the base form ‘was.' The verb ‘wasyo’ is intransitive because it does not require an object
argument. The inflection ‘yo’ (agreement)
with the verb
shows
that the action has happened in the past; this inflection also shows that
subject is singular in number. While for the plural subject, the inflection ‘yo’ (agreement) changes into ‘ya’ (agreement). This inflection
indicates that subject is masculine.
Future Simple
Tense
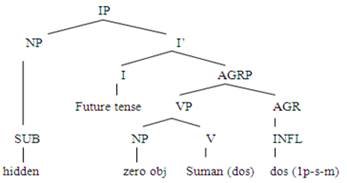
Example 11 Sumandos.
((I) will sleep.)
|
Null SUB |
sumandos |
|
Null SUB |
will sleep (future) |
|
SUB (null) |
V (1p-s-m) |
Figure 11
Tree Diagram
The
above tree diagram shows a sentence having zero subject and zero object in the
future simple tense with only (S)V in order. The verb ‘sumandos’ (will sleep) has been taken from the infinitive form ‘soman’
(to sleep) and the infinitive ‘soman’
(to sleep) is derived from the imperative form 'som’ (sleep). The phonological suffix ‘dos’ with the verb ‘somandos’
(will sleep) shows the future simple tense; it also indicates that the
hidden subject is the first person pronoun ‘ahon’
(I). If a subject is a second person pronoun subject, the inflection ‘dos’ (agreement) will change into ‘dohen’ (agreement), and if the subject
is third person, the inflection ‘dos’ (agreement)
will change into 'do.' The inflection
‘dos’ (agreement) shows the subject
is singular in number. In the case of the plural subject, the inflection ‘dos’ (agreement) will change into ‘daasen’ (agreement). This infection
also shows the masculine gender of the subject because the suffix ‘dos’ is used for masculine gender
agreement and ‘dias’ for feminine
gender agreement in the future tense in Sindhi/Lasi (Ali, Z., 2016).
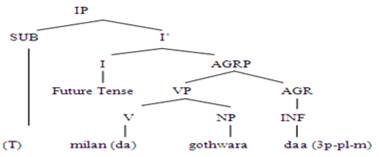
Example 12 Milanda goth wara. (Villagers will meet)
|
Milanda |
gothwara |
|
Will meet |
villagers |
|
V (pl-m) |
SUB (pl-m) |
Figure 12
Tree Diagram
The above tree diagram shows that the verb agrees in gender person and number with the subject. The statement structure is VS. The subject ‘goth wara’ (villagers) is plural in number and masculine in gender with a nominative case. The verb ‘melanda’ (will meet) has been taken from the infinitive form ‘melan’ (to meet) taken from the imperative form ‘mil’ (meet). The verb ‘melanda’ (will meet) is intransitive verb in this context in Lasi. The inflection ‘da’ (agreement) with verb ‘melanda’ (will meet) shows future tense of sentence. It also shows the first person of hidden pronoun subject. The inflection ‘da’ also shows the plural number of the subject. In case of singular subject, the inflection ‘daa’ will change into ‘do’. The inflection ‘da’ shows that subject is masculine in gender.
Findings
X Bar Theory by Haegeman (1994) has been applied to draw tree diagrams to represent Lasi sentences focusing on verb phrases, especially on INFL, to see the nature of the subject-verb agreement.
Number Agreement
The analysis of this study shows that in Lasi, the subject of the transitive and intransitive verbs in present tense occurs in the nominative case which determines the agreement. The inflections with transitive and intransitive verbs in indicative mood change according to the number of subjects. When the subject is singular, the verb terminates into sg- infliction ‘to’ (agreement) or ‘ti’ (agreement) but with a plural subject, the infliction ‘to’ changes into ‘taa’ (agreement); and inflection ‘ti’ (agreement) changes into ‘tiyon.' English uses inflections ‘s’ and ‘es’ to show plural subject (Aarts, 2011).
In past tense, when the subject is singular, the phonological inflection ‘o’ or ‘ee’ (agreement) is added with an intransitive verb. But in the case of the plural subject, the inflection ‘o’ changes into ‘aa’ and ‘ee’ changes into ‘yoon’ to show a number. However, the regular verb in English is only inflected with the morpheme' ed’ or ‘d’ for both singular and plural subjects in simple past tense (Haegemen, 1994).
Gender Agreement
The inflections that show the number of subjects also show the gender of subjects. In the case of the masculine subject, the conjugation with the verb is ‘to’ or ‘taa,' but with the feminine subject, the conjugation ‘to’ changes into ‘ti’ and the inflection ‘taa’ changes into ‘tiyoon’ (agreement). The interesting finding is that transitive verbs do not agree with subjects in the past but with objects. However, intransitive verbs do agree with their subjects. Phonological inflections “o” and “aa” show the masculine gender of subjects, and “ee” or “yoon” show the feminine gender. The inflections 'o', 'aa,' 'ee’, ‘yoon’ also show 1st, 2nd, and 3rd person of the subject.
Tense Agreement
The findings of this study show that the inflections in transitive and intransitive verbs indicate the tenses in Lasi; these are tense markers. Tense markers indicate time and action are performed (Ali, Bagddu & Maimota, 2014). It is found that the inflections ‘ti', 'to,' ‘tiyon’ and ‘taa’ with transitive and intransitive verbs are present as simple tense markers.
Conclusion
X bar theory of phrase structure is used to see the nature of the subject-verb agreement and sentence structure (word order) in Lasi. It is found that in Lasi, the transitive and intransitive verbs show full agreement with their subjects in the present, future simple tenses, and intransitive verbs agree with their objects in the past. Transitive and intransitive verbs in Lasi are inflected with many inflections (agreement markers); these inflections indicate the number, gender, and person of subjects along with the tense of the sentence. The verb in Lasi contains two inflections: the first one shows the person of its subject whereas the last inflection in the verb indicates the number, gender, and tense. However, the verb in English has two forms of the verb in present tense and one form in the past tense Haegeman (1994).
The basic word order of Sindhi/ Lasi, according to Allana (2010), is SOV. However, the speakers violate the word order spoken without affecting the meaning and form of the sentence. The result of this study explains that transitive or intransitive verbs agree with their subjects in terms of person, gender and number at both pre- and post-verbal positions.
References
- Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar. Oxford University Press.
- Ali, Z., & Muhammad, N. (2021). Code- Switching between Lasi and Urdu among Teachers at Secondary Level High School in Bela.
- Ali, Z., Bagddu, R.S., & Maimota, M.S. (2014). Tense and aspect in Hausa Language. Balochistan Journal of Linguistics, (2), 2312-5454
- Ali, Z., Khan, S. & Gulkhanda (2021). Article A Comparative Study of Locative, Source, Goal and Instrumentive Thematic Relations in English and Sindhi. University of Chitral Journal of Linguistics & Literature, 5(II), 237-255.
- Ali, Z., Roonjho, Z., & Brohi, F. M. (2021). A Comparison of the Lasi language with English. Progressive Research Journal of Arts & Humanities (PRJAH), 3(2).
- Allana, G. A. (2009). Sindhi Language and Literature at a glance (First ed.). Hyderabad, Pakistan: Sindhi Language Authority (SLA), Sindh, Pakistan.
- Allana, G. A. (2010). Sindhi Boli jo tashreehi grammar (A detailed grammar of the Sindhi Language) (First ed. Vol. 1). Sindhi Language Authority (SLA), Sindh, 71000, Pakistan.
- Alshammiry, K. (2016). Subject Verb Agreement in Modern Standard Arabic and Saudi Dialect of Arabic: A New Minimalist Account. International Journal of Language and Literature, 4(2).
- Amin, M., & Ali, Z. (2021). Phonological and Morphological Variations between Lasi and Standard Sindhi. Hor J. Hum. & Soc. Sci. Res, 3(2), 181-194.
- Baig, M. Q. (2006). Sindhi Grammar (Third ed. Vol. 1). Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan: Sindhi Adabi Board Kitaab Ghar, Tilk Charhi, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan.
- Baloch, N. B. (1962). Sindhi Boli ~ iaAdab Jee Tarikh (Third Edition). Pakistan Study Center, Sindh University, Jamshoro.
- Baloch, N. B. (2008). Belan ja Boal. Sindhi Sahat Ghar Rabia Siqure Gari Khoto, Hyderabad Sindh, Pakistan.
- Baloch, N. B. (2011). Sindhi Language,s past, present and future. Sindhi Boli Tahqeeqi Journal, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan., 4(3 & 4).
- Bauer, L. (1983). English Word-Formation. Cambridge University Press.
- Cole, J. S. (2001). Sindhi. Unpublished Manuscript: An Encyclopedia of the World's Major Lanuages. New York, NY: The H.W. Wilson Company.
- Corbett, G. (2003). Agreement: The range of the phenomenon and principles of the Surry Data Base of agreement. University of Surry.
- Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. (4th edition (March 14, 2013) ed. Vol. 1). USA.
- Das, P., & Madhumita Barbora. (2020). Derivational Morphology of Assamese Lexical Word Categories. Indian Journal of Language and Linguistics, 1-15.
- Devi, J. (2012). Implementing GF Resource Grammar for Sindhi-A subtitle that can be quite long if necessary (Master's thesis).
- Dixon, R. M. (2014). Making new words: Morphological derivation in English. Oxford University Press, USA.
- Grierson, G. A. (1919). Linguistic Survey of India, (Indo Aryan Family North- Western Group). Vol.8 (81-7536-373-8).
- Haegeman, L. (1994). Introduction to Government & Binding Theory (Second ed.). UK & USA: Blackwell Oxford UK & Cambridge USA.
- Hafiz, A. A. S. (2005). Verb agreement in standard arabic: An analysis in the minimalist program. Journal of Language and linguistics, vol-uno.1. 1475-8989.
- Jumani, N. B., & Lashari, M. A. (2011). Syntax in Action: The Verb Agreement in Sindhi Language. Language in India, 11(11) 9030-2940
- Kumar, R. (2011). Research Methodology: A step by step Guide for Beginners. Loss Angles, USA: SAGE
- Lashari, M. A., & Soomro. A. A. (2013). Subject Verb Agreement in Sindhi and English; A comparative study; Language in India,
- Lashari, M. A., Nirmal, & Gopang, I. B. (2013b). Insights into Subject-Verb Agreement in the Syntax of Sindhi and English Languages: A Critical and Comparative Analysis. Language in India, 13(7), 253-268.
- Pirzado, A. (2009). Sindhi Language and literature. Sindhi Language Authority, Hyderabad, Sindh: Sindhi Language Authority (SLA), Sindh, Pakistan.
- Pitafi, S. (2009). Evolution of writing Grammar in Sindhi (F. Hussain Ed. First ed.). Sindhi Language Authority (SLA), Sindh, Pakistan.
- Radford, A. (2004). Minimalist Syntax: Exploring the Structure of English (First Edition). University of Express
- Rahman, M. U., & Bhatti. (2009). Finite State Morphology and Sindhi Noun Inflections. Paper presented at the Conference on Language and Technology CLT09, Crulp, Lahore, Pakistan.
- Ranjan, R. (2016). Acquisition of ergative case in L2 Hindi-Urdu. University of Lowa.
- Stack, G. C. (2011). A Grammar of the Sindhi Language (F. Hussain Ed. First ed.). Sindhi Language Authority (SLA), Sindh, Pakistan.
- Surahio, F. A., & Jumani, A. K. (2016). Sindhi Morphological Analysis: An Algorithm for Sindhi Word Segmentation into Morpheme. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security (IJCSIS), 14(6).
- Trump, E. (2011). Sindhi Boli jo Grammar (A grammar of Sindhi Language) (A. S. Memon, Trans. V. H. Valabh, Fahmida. Ed. First ed.). Sindhi Language Authority (SLA), Sindh, Pakistan.
- Varshney, R. L. (1995). An introductory textbook of linguistics and phonetics. Rampur Bagh: Student Store.
- Veesar, Z. A., & Mustafa, G. (2021). A Comparative Analysis of Retroflexion in Romani and Lasi: NA. Journal of Education & Humanities Research, University of Balochistan, Quetta- Pakistan, 11(1), 78-95.
- Veesar, Z. A., Kadhim, K. A., & Bagudu, R. S. (2015c). The Most Prominent Theta Roles in the Sindhi Language: The Hierarchy. International Journal of Foreign Language Teaching and Research, 3(12), 11-24.
- Veesar, Z. A., Kadhim, K. A., & Sriniwass, S. (2015a). Establishing the Thematic Structure and Investigating the most Prominent Theta Roles Used in Sindhi Language. International Journal of Applied Linguistics and English Literature, 4(4), 216-230.
- Veesar, Z. A., Kadhim, K. A., Shah, S. A., & Khuhro, R. A. (2016). Argument Structure of Sindhi Verbs: An Analysis of Thematic Relations. Language in India, 16(2)
- Veesar, Z. A., Sriniwass, S., & Kadhim, K. A. (2015b). A Comparison of Theme Theta Roles in English and Sindhi. Language & Communication, 2(1), 77-89.
- Zahid, A. (2016). Morphosemantic and syntactic analysis of verbs in Sindhi/Zahid Ali (Doctoral dissertation, University of Malaya).
Cite this article
-
APA : Azam, M., Ali, Z., & Shahida. (2022). Subject-Verb Agreement in Lasi and English: A Morphosyntactic Analysis. Global Language Review, VII(II), 37 - 54. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2022(VII-II).04
-
CHICAGO : Azam, Muhammad, Zahid Ali, and Shahida. 2022. "Subject-Verb Agreement in Lasi and English: A Morphosyntactic Analysis." Global Language Review, VII (II): 37 - 54 doi: 10.31703/glr.2022(VII-II).04
-
HARVARD : AZAM, M., ALI, Z. & SHAHIDA. 2022. Subject-Verb Agreement in Lasi and English: A Morphosyntactic Analysis. Global Language Review, VII, 37 - 54.
-
MHRA : Azam, Muhammad, Zahid Ali, and Shahida. 2022. "Subject-Verb Agreement in Lasi and English: A Morphosyntactic Analysis." Global Language Review, VII: 37 - 54
-
MLA : Azam, Muhammad, Zahid Ali, and Shahida. "Subject-Verb Agreement in Lasi and English: A Morphosyntactic Analysis." Global Language Review, VII.II (2022): 37 - 54 Print.
-
OXFORD : Azam, Muhammad, Ali, Zahid, and Shahida, (2022), "Subject-Verb Agreement in Lasi and English: A Morphosyntactic Analysis", Global Language Review, VII (II), 37 - 54
-
TURABIAN : Azam, Muhammad, Zahid Ali, and Shahida. "Subject-Verb Agreement in Lasi and English: A Morphosyntactic Analysis." Global Language Review VII, no. II (2022): 37 - 54. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2022(VII-II).04