Abstract
The Pandemic COVID-19, though challenged systems but provided them with opportunities to address languages them. Pedagogical innovations were put forward, and traditions also paved the way for learning. This article describes the effectiveness of the mixture (bilingualism) of Urdu and English that how it helps the undergrads (major is English) to develop an understanding of the content knowledge and further various skills. The study was focused on 140 undergrads of a public sector university to get their feedback on the best possible language-speaking practices for enhancing content knowledge and skills. The study, based on the results of a shared questionnaire, concludes that for online teaching, the blend of Urdu and English languages is more helpful instead of the monolingual approach to improving literary and linguistics areas. It also recommends that this can also be practised during face to face teaching to realize the objectives of the academic programs.
Key Words
Pedagogical Interventions, Undergrad Level, Bilingualism, Urdu and English Mixture
Introduction
Over the years, there have been debates and discussions that there is the effectiveness of bilingualism in classroom proceedings both at secondary and tertiary education with regard to language learning, cultural awareness, identification and learning of new attitudes, etc. (Archila & Truscott de Mejía, 2017; Baker & Wright, 2017; Dewaele, Housen, & Wei, 2003; García, Lin, & May 2017; Palfreymen & van der Valt, 2017).
Even in the present time, there is a difference of opinion among the educationists supporting bilingualism or otherwise, but the Pandemic COVID-19 has forwarded new ideas, approaches, and techniques beneficial for enhancing content knowledge at the undergrad level during teaching online. At the same time, it has invited the researchers to devise innovative techniques irrespective of their names or nature but must be effective for transferring knowledge and improving various skills of the undergrads.
This descriptive study is the outcome of the same motivation that to what extent something new could be effective for the undergrads with major in English to understand content knowledge based on English literature and Linguistics as generally it is assumed that the appropriate approach for undergrads to get them enabled to enhancing content understanding and improving skills is the use of foreign language.
Research Objective
The main objective of the study is to know whether the mixture (bilingualism) of Urdu and English languages during online
Literature Review
Pronouncing that single or more than two languages’ speakers have more improved mental cutoff points than speakers of a single language is irrefutably not a nostalgic case; in any case, one affirmed by genuine assessments provoked courtesy the point. The 1989 allocation of (Foster and Reeves, 1989), for example, applied tests so far as the assessment of metacognitive areas is concerned in a party of English-French bilinguals getting heading in French and the benchmark get-together of English speakers. They contemplated the disclosures that the understudies who had gotten dull tongue heading scored higher on tasks including assessment which is the most fundamental smart ability as shown by Bloom's shrewd depiction. The fast model appraisal showed that the understudies who had considered French the longest played out the best.
There is adequate evidence that, around the world, speaking more than two languages is the norm and speaker of one language is the exception (Chumbow, 2009), and the advantages of bilingualism and multilingualism ought to be recognized, manhandled, and used for the solitary turn of events and unforeseen public development. This part doesn't harp in transit that speaker or a language or more languages are more gainful than being a speaker of a language; it rather surveys a degree of multidimensional certifications that have been set up from moved investigation disclosures, featuring the advantages of bilingualism in people or plurilingualism and multilingualism in various social orders. It explores the wonder of bilingualism and multilingualism, how it very well may be a "liking" and not a "condemn" at the two levels of its sign. The part is in this manner ordinarily a diagram of observational affirmation of the upsides of individual and social bilingualism/multilingualism and semantic arrangement of countries as setting up by research revelations over the most recent numerous years from concentrates by language topic specialists and subject matter experts, for example, Byram (1997); (Baker et al., 1998); Bialystok et al., 2007); Ewert, 2006); Paradowski et al., 2009); Grin et al., 2013, and so forth, For instance, an assessment did by Kessler and Quinn, 1987) on grade 6 understudies (monolingual English talking and bilingual Spanish and English talking social affairs), utilizing both normalized investigating and imparted test, contemplated the revelations that the bilinguals dwarfed the monolinguals in passing on more unpredictable theories. They made an interpretation of their openings to infer that the complexities of the language updates of the bilinguals are occasioned by their ability to attempt joined high thinking development, and this relates to a property obliged by most bilinguals from their explored people. This sharp quality in bilinguals outfits them with the concluded potential to be non-mentioning in their appearances, as later got by Baker's (2003) ensure that the bilinguals are "innovative" in nature. In addition, their open affectability, which was crucial for the openings of Kessler and Quinn (Kessler and Quinn, 1987), May et al., 2004), sees that the multilingual, by uprightness of their specific language experiences, have high conviction and more grounded energy to introduce unafraid of building non-especially spread out verbalizations.
There have been some studies reflecting positive effects of bilingualism so far as the students’ high cognitive skills are concerned and proved to have vast possibilities for those completing higher studies in bi/multilingual settings (Vygotsky, 1978). It is intriguing to take note that bilingual guidance for some methodology makers isn't simply transforming into an esteemed need at the pre and school level everywhere in the world (Zakharia, 2017).
Information on a subsequent language additionally appears to harmonize with high scholastic accomplishment. An examination by Horn and Kojaku (2001) shows that understudies who were in "exhaustive" programs in auxiliary school, which included 3 years of obscure lingo study, will undoubtedly gain better assessments in school and more loath to slacker. This discovering calls attention that speakers of two languages have the possibilities to accomplish high savvy rules with less exertion than monolinguals. This position is made by Curtain and Dahlberg (2004), who expresses that the accommodating delayed consequence of social data is everything seen as animated when that data is skilled through faint dialect and joined by encounters in socially clear conditions. Thus, encounters in learning an after language and learning another culture will engage educators' joint endeavors with their understudies' learning experience. In like manner, talented instructors understand that a positive self-thought and a positive evident confirmation with one's way of life are the reason for scholastic achievement.
Belhiah and Elhami's (2015) base on 500 L1 Arabic speakers and 100 teachers in six schools in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, Oman, and Saudi Arabia found that understudies and educators on a chief level got a kick out of the opportunity to assemble in both a dim tongue (English) and Arabic. For instance, the creators fight that with the understudies' low cutoff level in English, it is more fit to have a two dialects technique as such, the understudies would improve in English and at the same time be less disappointed in learning their point.
Investigation in the twentieth century displays that, from one point of view, talking in more than one language puzzles the understudy (Baker and Wright, 2017) while on different understudies talking and moving more than a language is 'more impressive', have further developed insightful limits, and can all the practically certain cycle data from the climate and in this manner show a more conspicuous proportion of a cutoff concerning learning than that of monolinguals (Bartolottie and Marian, 2012; Bhattacharjee, 2012; Baker and Wright, 2017; Dooly, 2007).
As of late, nonetheless, Dearden (2016, among others) noticed that in an investigation did on 55 Western and Eastern nations that, despite the fact that students and educators supported EMI, more normal in private foundations, be that as it may, they would lean toward having the public language close by English and in this manner bilingual guidance.
Regardless, English as a single approach to teaching at school or tertiary levels has been tended to concerning its capacity and quality in the hour of globalization. During the late nineteenth century and all through the twentieth century, particularly after the 1960s with released up progress to Europe and the United States, different schools everything considered are satisfying people's high longings of including home tongues, for example, Spanish, German, Italian, in which some substance subjects are told (Gandara and Escamilla, 2017). This breaker, recommended as passing bilingual coordinating (TBE), English genuinely remains the titanic section of bearing, yet various tongues are emerging.
While two dialects as the vehicle of direction have not met with much positivism in some high-level training associations, it is also in others, for instance, in Finland where such courses are taught in Finnish, and moreover Swedish and English (Anckar, 2006; Källkvist and Hult, 2014), and in Switzerland and Freiburg, Langner and Imbach (2000). Plessis (2006) pin focuses in the said conversation that this mix of vernaculars as an approach to managing scholastic heading in South Africa in obvious level getting ready is 'flexible discovering its sensibility, and notes three sorts: Dual-Medium Education (DME), Parallel-Medium Education (PME) and English-Medium Instruction several dialects are given in unequivocal classes or two tongues are given in a general class truly like the case in Sweden. (Källkvist and Hult, 2014).
Scholastic benefits because of multilingual capability are briefly caught in Moore's (2011) follow-up report in Language Matters: "… the absence of language abilities limits scientists in their capacity to connect universally in or with their exploration, and in their profession openings." This is an all-around established experimental benefit, for a specialist who is monolingual is restricted, of course, from getting to vital examination discoveries of researchers of other etymological foundations from his. If so, there is no uncertainty that such scientists will be impeded in their scholarly profession because of restricted proficiency and abstract materials openness. Nieto (1999) all the more relevantly propels the benefits of multilingualism in the scholarly community, proposing that "multicultural schooling will eventually be decided by its prosperity or in any case in being partnered to 'superior grade' and 'exclusive expectations' of training. While multicultural training may effectively expand social and social mindfulness and animate basic reasoning abilities, an entire educational plan approach should likewise show greatness in conveying fundamental abilities, information and understandings. It is in a comparable light that Cummins (2000) battles for an approach to managing "phenomenal instructional technique" containing (1) tutoring grounded in the existences of understudies, which is (2) multicultural, antiracist, and consistent of significant worth, (3) participatory and experiential, (4) instructively comprehensive with raised presumptions for execution, and (5) socially touchy. He suggests that (6) understudies should get fundamental in approach, (7) empowering them to have a conviction that everything is acceptable, gigantic, and anxious to share contemplations and assessments, and (8) dynamic in pushing social change and worth.
Multiculturalism has, as one establishment, the ideal of same, satisfying, for the most part, benevolent presence of assembled languages, and of various demanding, social and ethnic parties in a pluralist society. A multicultural perspective is more than halfway settled on the probability that an individual can suitably hold on any occasion, two social characters. From a substitute point of view, it is conceivable to be a part of the hyphenated two groups. In this sense, identities are joined; the parts become another entire and the solitary changes into a basically integrated combination of the parts (Baker, 2003).
Findings
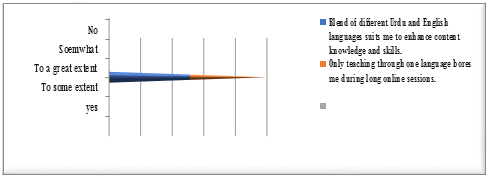
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Discussion
The study aimed to answer the following queries with an objective to know whether the mixture (bilingualism) of Urdu and English languages during online teaching/learning is effective for the undergrads having English as a major to enhance their understanding of the content knowledge and further their skills or the use of single language (English) is better than such blend.
1. There must only be single language use during online teaching for enhancing content knowledge and skills at the undergrad level.
2. The blend of Urdu and English (bilingualism) is the need of time so far as massive online classes are concerned to make teaching result oriented.
3. The blend of Urdu and English (bilingualism) is very effective for the undergrads having a major in English to enhance content knowledge and improve other skills.
Generally, it is seen that our emotions, feelings and other difficult ideas are easily communicated and understood when said in the speaker’s own language, and almost there’s hardly any shyness on the part of the speaker while communicating them, but if the same stuff is made mandatory to be said in the foreign language, the speaker is sent to the straight jacket.
The first query has had many debates, especially in our educational set up because of the importance of the English language, which has its historical significance. Even in today’s world, there is no land on the globe where we cannot find speakers of the English language; whether they are fluent or not is another debate. In our education system, almost the institutions of higher education claim that they promote English as a language through which classroom proceedings are conducted, but the recent Pandemic has not only exposed the claim but has also invited our attention to other successful practice if realized. The question has been answered quite fairly by the respondent when a majority says that there must not be a single language for classroom proceedings, and this could have been the outcome of many reasons which the respondents considered such as time, internet connectivity, much matter with less time to comprehend, too many classes, etc. For instance, they are quite comfortable when the blend of Urdu and English (bilingualism) is used, which, in their opinion, is the need of time so far as massive online classes are concerned to make teaching result oriented. There’s no denying the fact that today’s undergrads have many opportunities to learn a foreign language because of massive online language programs and material available on the Internet; however, it’s very important that during the online classes they are not only to learn ideas related to linguistics and literature, but many other skills required for assessment; knowledge and skills run parallel.
Two of the important questions (of the questionnaire) were: students feel shy while speaking English during online classes, and students like the blend of Urdu and English during online classes, the responses of which have been reflected in figure No. 2. The former comments on the overall attitude of most of the undergrads mostly observed in and outside the academic institutions, whereas the latter further highlights the possible reason for the first. It is hardly observed that such subjects are engaged in speaking a foreign language outside their classroom except for some chunks of language items with a blend of Urdu and English or sometimes their mother tongue that could be Punjabi or local dialect but are left on either English language or a blend of Urdu and English so far as online classes are concerned. There’s also a possibility that there are some students who possess clarity of ideas but cannot express themselves because of foreign language hindrance, which could be minimized if allowed to speak Urdu or a blend of Urdu and English language. This has also been noticed, in the light of the findings, that there’s some sort of reluctance on the part of subjects because when the ideas are communicated by the instructor in Urdu, they are in a better position to understand the subject matter. This is what the responses of the subjects related to their understanding of content knowledge, which a majority believe is the ultimate of any academic program. Figure No. 3 elaborates much to answer the above reasons of being shy while speaking shy it has been found that the majority of respondents feel that students don’t possess good listening skills of English creating difficulty for them to comprehend the content, which affects their understanding. The improper understanding of the content knowledge definitely does not pave for them to further their skills. It further throws light on the environment, which, according to the subjects, becomes boring when proceedings are always in a single foreign language. In other words, such an environment nether remains conducive for neither earning nor result-oriented because of the lingual monotony, as is clear in Figure No. 4.
It is also assumed that lively classrooms are encouraged by almost all educationists, which guaranteed when there’s interaction between the teacher and the taught. But during online classes, this can prove a blow to knowledge transfer to students if they feel boredom during long hours of online learning. Hence, the only way left for the instructors is to use a blend of Urdu and English so that they may engage the students without letting them bored to comprehend what is said and desired for future academic achievements.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In the light of the results of the study concludes that the major objective of any academic program is to enhance content knowledge and skills, which needs result-oriented teaching techniques for which it is possible that the educators have to change the strict lingual belief for the undergrads whose major is English to ensure maximum understanding of content knowledge that might pave the way to improve their different skills and it can be said, in the light of the results, that bilingual approach for such graduates could be effective at least during present academic hard times. The mixed approach may provide them with an easy environment for learning in which almost every undergrad could contribute without having any foreign language speaking fear or anxiety. The study concludes that there must not be single language use during online teaching for enhancing the content knowledge and skills of the undergrads with English as a major and recommends that:
1. During online classes, a mixture (bilingualism) of Urdu and English for the undergrads with a major in English could be encouraged during online classes.
2. Students may be given maximum opportunity to express themselves in either language or bilingually.
3. A bilingual approach could also be practised, with care, during face to face teaching/learning conditions to develop students’ confidence.
4. Students’ overall understanding of the content knowledge may be given priority instead of the language they use.
5. For enhancing foreign language proficiency, special classroom fun learning games can be promoted to avoid bilingualism as a permanent way of teaching to undergrads with English as a major.
6. Instructors engaged in teaching undergrads with a major in English may use bilingual approach as a means to achieve academic ends instead of sticking to the sole approach.
References
- Anckar, O. (2006). University Education in a Bilingual Country: The Case of Finland. Higher Education in Europe, 25(4), 499-506.
- Archila, P. A., & Truscott de MejÃÂa, A. M. (2017). Bilingual University Science Courses: A Questionnaire on Professors' Practices and Espoused Beliefs. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism, Online June 2017.
- Baker, C. (2003). Foundations of bilingual education and bilingualism. (Vol. 27). In: Multilingual Matters. Buffalo, Toronto: Clarendon;
- Baker, C., & Wright, W. (2017). Foundations of Bilingualism and Bilingual Education (6th ed.). Clevedon, UK: Multilingual matters.
- Baker, C., Jones, S. P. (1998). editors. Encyclopedia of bilingualism and bilingual education. In: Multilingual Matters.
- Bartolottie, J., & Marian, V. (2012). Language Learning and Control in Monolinguals and Bilinguals. Cognitive Science, 36, 1129-1147.
- Belhiah, H., & Elhami, M. (2015). English As a Medium of Instruction in the Gulf: When Students and Teachers Speak. Language Policy, 14(1), 3-23.
- Bialystok, E., Craik, F. I., & Freedman, M. (2007). Bilingualism as a protection against the onset of symptoms of dementia. Neuropsychologia. 45(2), 459-464.
- Byram, M. (1997). Teaching and Assessing Intercultural Communicative Competence. Multilingual Matters;
- Cummins, J., Language, P., & Pedagogy. (2000). Bilingual Children in the Crossfire (Vol. 23). Multilingual Matters
- Curtain, H. A., & Dahlberg, C. A. (2004). Languages and Children, Making the Match: New Languages for Young Learners. Allyn & Bacon
- Dearden, J. (2016). A report on the Global Phenomenon of EMI: A Bird's Eye View of EMI In 55 Countries. Research. The British Council, 2-34.
- Dewaele, J. M., Housen, A., & Wei, L. (2003). Bilingualism: Beyond Basic Principles. In honor of H. B. Beardsmore. Clevedon, UK: Multilingual Matters.
- Dooly, M. (2007). Constructing Differences: A Qualitative Analysis of Teachers' Perspectives on Linguistic and Cultural Diversity. Linguistics and Education, 18(2), 142-166.
- Ewert, A. (2008). syntactic preferences of polish adolescents in bilingual and monolingual education programmes. Morphosyntactic issues in second. Language Acquisition. 29:47
- Foster, K. M., & Reeves, C. K. (1989). Foreign language in the elementary school (FLES) improves cognitive skills. FLES News. 2(3), 4
- Gandara, P., & Escamilla, K. (2017). Bilingual Education in the United States. In Bilingual and Multilingual Education, 1-16. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing.
- GarcÃÂa O., Lin, A., & May, S. (2017). Bilingual and Multilingual Education. Encyclopaedia of Language and Education (3rd ed.). Springer, Cham.
- GarcÃÂa, A. L., & May, S. (Eds.), Bilingual and Multilingual Education. Encyclopaedia of Language and Education (3rd ed.). Springer, Cham.
- Grin, F., & Gazzola, M. (2013). Assessing efficiency and fairness in multilingual communication: Theory and application through indicators. In: Berthoud A-C, Grin F, Lüdi G, editors. Exploring the Dynamics of Multilingualism. Amsterdam: John Benjamins. pp. 365-386
- Horn, L., & Kojaku, L. K. (2001). High School Academic Curriculum and the Persistence Path through College: Persistence and Transfer Behavior of Undergraduates 3 Years after Entering 4-Year Institutions (NCES 2001-163). Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics;
- Kessler, C., & Quinn, M. E. (1987). Language minority children's linguistic and cognitive creativity. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development. 8:173-186
- Langner, M., & Imbach, R. (2000). The University of Freiburge: A Model for a Bilingual University. Higher Education in Europe, 25(4), 461-468.
- MacmiKällkvist, M., & Hult, F. M. (2014). Discursive Mechanisms and Human Agency in Language Policy Formation: Negotiating Bilingualism and Parallel Language Use at a Swedish University. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism, 19(1), 1-17.
- May, D. R., Gilson, R. L., & Harter, L. M. (2004). The psychological conditions of meaningfulness, safetyand availability and the engagement of the human spirit at work. Journal of Occupationaland Organizational Psychology, 77, 11-37
- Moore, P. (2011). Collaborative interaction in turn-taking: A comparative study of European bilingual (CLIL) and mainstream (MS) foreign language learners in early secondary education. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. 14(5), 531-549
- Nieto, S. (1999). The Light in their Eyes: Creating Multicultural Learning Communities. New York: Teachers College Press. Creating and Digitizing Language Corpora. Palgrave Macmillan, London
- Palfreymen, D. M., & Van der Walt, C. (2017). Academic Biliteracies: Multilingual Repertoires in Higher Education. Bristol, Multilingual Matters.
- Paradowski, M. B., Cook, V. J. (2009). Rola native speakera w nauczaniu języków obcych. Perspektywa pedagogiczna, psychologiczna i praktyczna. Kształcenie językowe w szkolnictwie wyższym Warsaw: Academica; 163-188
- Plessis, T. (2006). From Monolingual to Bilingual Higher Education: The Repositioning of Historically Afrikaans-Medium Universities of South Africa. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism, 5(1), 87-113.
- Vygotsky, L. (1978). Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Psychological Processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Zakharia, Z. (2017). Bilingual Education in the Middle East and North Africa. In O.
Cite this article
-
APA : Rasool, G., Nadeem, M., & Abid, M. A. (2020). Effectiveness of the Mixture (Bilingualism) of Urdu and English for Enhancing Content Knowledge Understanding at Undergrad Level. Global Language Review, V(IV), 65-73. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2020(V-IV).08
-
CHICAGO : Rasool, Ghulam, Mubashar Nadeem, and Muhammad Amjad Abid. 2020. "Effectiveness of the Mixture (Bilingualism) of Urdu and English for Enhancing Content Knowledge Understanding at Undergrad Level." Global Language Review, V (IV): 65-73 doi: 10.31703/glr.2020(V-IV).08
-
HARVARD : RASOOL, G., NADEEM, M. & ABID, M. A. 2020. Effectiveness of the Mixture (Bilingualism) of Urdu and English for Enhancing Content Knowledge Understanding at Undergrad Level. Global Language Review, V, 65-73.
-
MHRA : Rasool, Ghulam, Mubashar Nadeem, and Muhammad Amjad Abid. 2020. "Effectiveness of the Mixture (Bilingualism) of Urdu and English for Enhancing Content Knowledge Understanding at Undergrad Level." Global Language Review, V: 65-73
-
MLA : Rasool, Ghulam, Mubashar Nadeem, and Muhammad Amjad Abid. "Effectiveness of the Mixture (Bilingualism) of Urdu and English for Enhancing Content Knowledge Understanding at Undergrad Level." Global Language Review, V.IV (2020): 65-73 Print.
-
OXFORD : Rasool, Ghulam, Nadeem, Mubashar, and Abid, Muhammad Amjad (2020), "Effectiveness of the Mixture (Bilingualism) of Urdu and English for Enhancing Content Knowledge Understanding at Undergrad Level", Global Language Review, V (IV), 65-73
-
TURABIAN : Rasool, Ghulam, Mubashar Nadeem, and Muhammad Amjad Abid. "Effectiveness of the Mixture (Bilingualism) of Urdu and English for Enhancing Content Knowledge Understanding at Undergrad Level." Global Language Review V, no. IV (2020): 65-73. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2020(V-IV).08